2. Operations and Governance
In response to the rapidly changing global economic environment and industry trends, Quanta continues to uphold steady management and forward-looking planning as core principles, while strengthening corporate governance mechanisms and operational resilience to enhance overall competitiveness and sustainable value. By implementing business integrity, establishing a robust risk management framework, deepening stakeholder engagement, and enhancing information transparency, Quanta is committed to building a high-performance and highly transparent governance system. This ensures that while pursuing operational growth, the Company also upholds its Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) responsibilities, thereby fostering a trustworthy global corporate image.
2.1. Corporate Governance
Quanta regards corporate governance as the cornerstone of sound operations and sustainable development. The Company continuously strengthens its governance framework and internal control systems, enhances the functionality and transparency of the Board of Directors, and ensures that operations adhere to the principles of integrity, accountability, and efficiency. Through a well-established supervisory mechanism, a diversified Board of Directors composition, and the operation of functional committees, Quanta implements governance objectives, strengthens trust with stakeholders, and builds a resilient and forward-looking corporate structure.
2.1.1. Board of Directors Operations
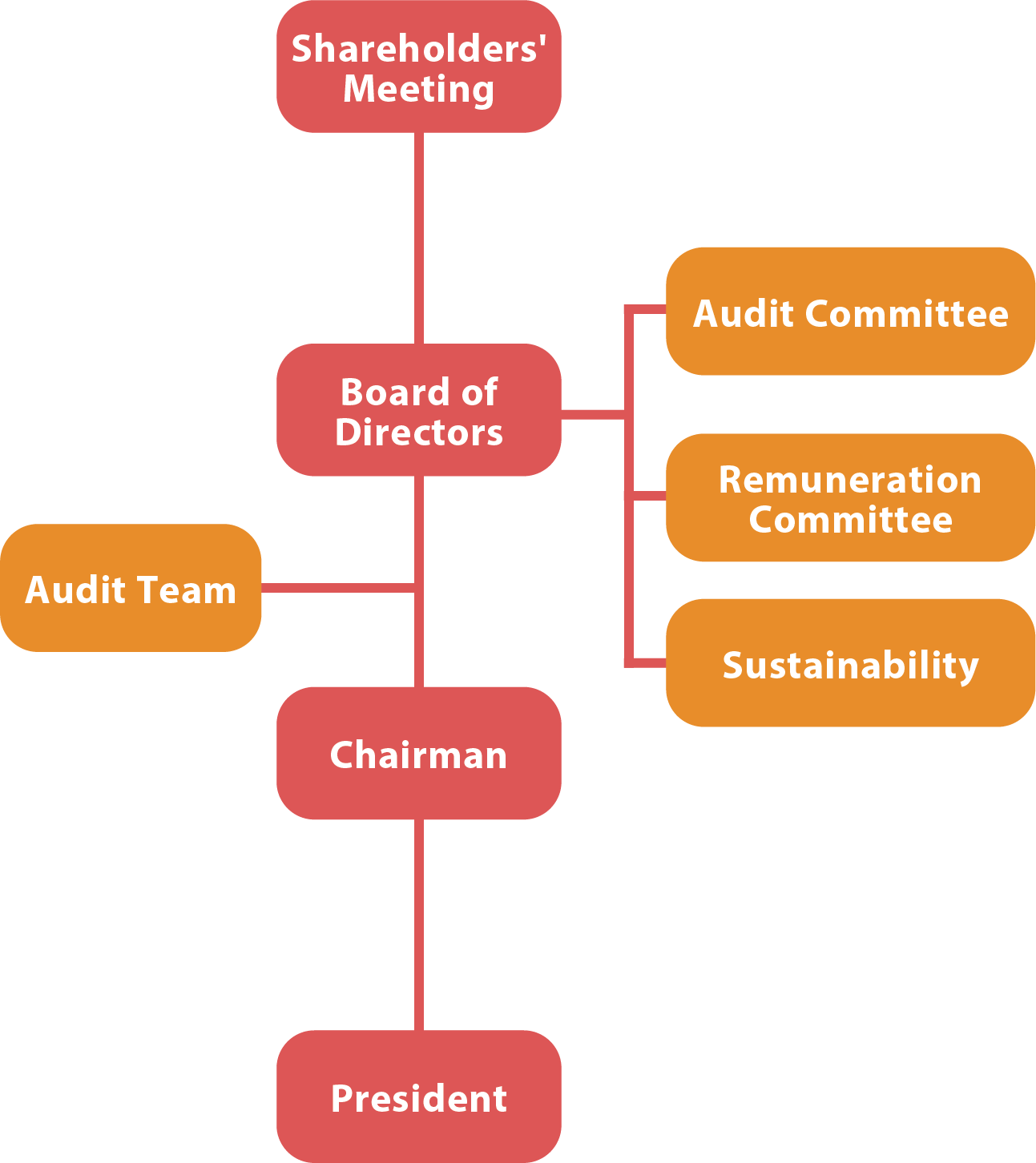
The Board of Directors serves as the Company's highest governance body, responsible for overseeing the management team to ensure compliance with laws and regulations, enhancing information transparency, and implementing corporate responsibility. Board members leverage their diverse backgrounds and extensive experience to provide guidance on major corporate decisions, helping to prevent value-damaging policies, safeguard shareholder interests, and enhance governance effectiveness. Quanta continues to optimize the governance structure of the Board of Directors, advancing the professionalism and diversity of board members to improve overall decisionmaking quality and supervisory effectiveness. Since 2019, the Company has appointed a Corporate Governance Officer responsible for ensuring procedural compliance in the operations of the Board of Directors and the Shareholders' Meeting, thereby promoting transparency and adherence to relevant regulations.
The Board of Directors convenes meetings at least once per quarter as stipulated. The management team regularly reports to the Board on business operations, development strategies, and sustainability-related topics-such as the Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi), net-zero planning, business integrity, information security, material topics, and stakeholder engagement-ensuring a robust communication mechanism. In 2024, a total of six Board meetings were held, with an average attendance rate of 95.2% by the directors, demonstrating their active commitment to governance duties. For details of the Board of Directors' attendance in 2024, please refer to section "2.3.1 Operation of the Board of Directors" in the Company's Annual Report.
Director Nomination and Appointment
The Board of Directors, as the Company's highest governance body, is composed of five to nine members as stipulated in the "Articles of Incorporation". Board member nominations and selections are conducted under a candidate nomination system in accordance with the "Articles of Incorporation". In addition to evaluating candidates' academic and professional qualifications, the process also takes into account stakeholder input and complies with the "Director Election Procedures" and the "Corporate Governance Code", to ensure the Board remains effective, collaborative, diverse, and aligned with corporate needs.
The current Board of Directors consists of seven members, including three independent directors. An Audit Committee has been established, with independent directors serving as members to perform the duties of supervisors. The nomination of independent director candidates follows the regulations set forth in the "Regulations Governing Appointment of Independent Directors and Compliance Matters for Public Companies", and includes independence assessments to strengthen governance functions and the objectivity of the Board of Directors. To enhance decision-making quality and supervisory effectiveness, the Company regularly reviews the structure and operational performance of the Board of Directors. Through continuing education and performance evaluation mechanisms, it ensures that directors continuously enhance their professional capabilities and diligently fulfill their governance responsibilities.
Composition and Diversity of the Board of Directors
Quanta has established a "Corporate Governance Code", which clearly defines the "competencies that the Board of Directors as a whole should possess." The Board of Directors is accountable to the shareholders' meeting, and the various operations and arrangements of the corporate governance system must ensure that the Board exercises its powers in accordance with laws, the company's articles of incorporation, or resolutions of the shareholders' meeting. The composition of the Board of Directors incorporates appropriate diversity considerations, including fundamental elements such as gender equality, age, nationality, and cultural background, as well as professional expertise and experience. In addition to possessing professional backgrounds and skills, board members should also have expertise in the Company's business planning and operations. In alignment with these principles, the Company has set a target of appointing at least one female director and ensuring a minimum of two directors with expertise in finance and accounting. The Company also continues to implement a Board succession plan, cultivating internal talent and maintaining a candidate database to support future board appointments.
The current (14th) Board of Directors consists of seven directors, including one female director, accounting for 14% of the seats. Among the board members, those who do not hold employee status account for 57% of the board seats; independent directors account for 43% of the board, meeting the minimum requirement of three seats. In terms of tenure, one director has served for less than three years, one for three to six years, and one for six to nine years. No director has served more than three consecutive terms. The age distribution of the Board shows that five directors are over the age of 70, while two are under the age of 60. There are no second-degree kinship relationships among board members. The Board collectively possesses professional expertise spanning information technology, electronic manufacturing, finance, law, and business management, equipping them with the capabilities to address global market demands and sustainability challenges. The diversification is as follows:
| Position | Name | Basic Composition | Professional Knowledge & Expertise | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nationality | Gender | Employee of the Company | Age (years) | Tem of office of Independent Director (years) | Technology Industry | Enterprise Management | Finance and Accounting | Risk Management | Sustainable Development | Financial Investment | Research & Development in Technology | ||
| Chairman | Barry Lam | Citizen of the Republic of China (R.O.C) | Male | >70 | – | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Vice Chairman | C. C. Leung | Male | ✓ | >70 | - | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Director | C. T. Huang | Male | ✓ | >70 | - | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Director | Elton Yang | Male | ✓ | 61~70 | - | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Independent Director | Hung Ching Lee | Male | 51-60 | 3-6 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Independent Director | Dr. Pisin Chen | Male | >70 | 6-9 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||
| Independent Director | Su-Pi Shen | Female | >70 | 3以下 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
Board of Directors Performance Evaluation
To enhance corporate governance and continuously improve the effectiveness of the Board's operations, Quanta has established the "Regulations for the Performance Evaluation of the Board of Directors and Functional Committees" as the institutional framework for performance assessments. The Board of Directors and functional committees conduct an annual performance evaluation at the end of each fiscal year based on established assessment indicators, completing the process before the end of the first quarter of the following year. This ensures that the operations of the Board of Directors not only comply with relevant laws and regulations but also follow best governance practices. In addition, at least once every three years, an external independent organization or professional is commissioned to conduct an external evaluation to ensure the process is objective, professional, and results in continuous improvement. The most recent external evaluation was conducted in 2022, with the next scheduled for November 2025. The results will be disclosed in the Company's next annual report. For detailed implementation status and subsequent improvement measures, please refer to sections "2.3.1.1 Board of Directors Evaluation Implementation Status" and "2.3.1.2 Objectives and Implementation Status of StrengtheningBoard of Directors Functions for the Current and Recent Years" of the Company's Annual Report.
Compensation of Directors and Senior Executives
The Company's policy on directors' and employees' compensation is stipulated in Article 27 of the Company's Articles of Incorporation: When the Company reports a profit in its annual final accounts, no less than 2% of the profit shall be allocated as employee remuneration, and no more than 2% as directors' compensation. In the event of accumulated losses, such losses must first be covered before any distribution. Employee remuneration may be distributed in the form of cash or shares, and eligible recipients may include employees of subsidiaries, subject to criteria established by the Board of Directors. Directors' compensation is paid in cash. Although only fixed remuneration is currently granted, Quanta has established the "Regulations for the Performance Evaluation of the Board of Directors and Functional Committees" to conduct regular selfevaluations by both directors and relevant executive units. The evaluation results are submitted to the Remuneration Committee and the Board of Directors for review, serving as a reference for determining variable compensation.
The Company's managerial compensation is determined in accordance with the "Regulations on the Remuneration of Directors and Managers", taking into account job titles, educational and professional backgrounds, competencies, and responsibilities. In addition, reference is made to the Taiwan human resources market, industry standards, and the Company's salary and benefits policies. Performance evaluations are conducted pursuant to the "Regulations on the Performance Management of Directors and Managers", covering six indicators: mastery of company goals and tasks, understanding of responsibilities, degree of participation in operations, internal relationship management and communication, professionalism and continuous development, and internal control. Additional special contributions are also considered. Performance evaluation results serve as a reference for determining individual remuneration. The composition of compensation is defined in accordance with the Organizational Rules of the Remuneration Committee, and its scope aligns with the disclosure requirements for directors' and managers' compensation as stipulated in the "Regulations Governing Information to be Published in Annual Reports of Public Companies".
Senior executive compensation consists of a fixed salary and variable incentives. Determination of compensation is based on job level, educational and professional background, competencies, and responsibilities, with reference to market benchmarks and the Company's internal compensation policies. Variable compensation is determined in accordance with the "Regulations on the Performance Management of Directors and Managers", with evaluations covering operational participation, goal achievement, communication and collaboration, professional development, and compliance with internal controls. Overall contribution and value are also considered. Since 2023, Quanta has formally incorporated sustainability performance into the variable compensation structure for senior executives. The evaluation encompasses three core dimensions: environmental impact, sustainable talent development, and corporate diversity and inclusion. Performance in these areas is linked to a variable salary adjustment range of plus or minus 10%. By integrating ESG indicators into the executive compensation mechanism, the Company enhances management's focus on and responsiveness to sustainability issues, facilitates the translation of sustainability strategies into measurable performance objectives, and strengthens the Company's ability to address potential risks such as climate change, talent retention, and social inclusion-thereby reinforcing overall resilience and long-term competitiveness.
| Dimension | Description |
|---|---|
| Environmental Impact | Covers progress in achieving environmental goals, including greenhouse gas reduction, energy efficiency, water resource management, and waste management. |
| Sustainable Talent Development | Includes retention of key talent, employee training, employee engagement, and strengthening of organizational culture. |
| Corporate Diversity and Inclusion | Focuses on gender equality, inclusive leadership, support for disadvantaged groups, and the development of diverse talent. |
The remuneration for directors and senior executives is proposed by the responsible units based on their level of operational involvement and performance, and after review by the Remuneration Committee, the proposal is submitted to the Board of Directors for approval. Senior executives undergo performance evaluations twice annually, conducted through self-assessments, supervisor reviews, and comprehensive departmental assessments. In addition to operational indicators, the evaluations incorporate nonfinancial aspects such as core value implementation, risk management, sustainability engagement, and continuous professional development. Please refer to section "2.2.4 Remuneration Policy" of the Company's Annual Report for further details.
Conflict of Interest Management
Quanta has established clear conflict of interest avoidance provisions in accordance with the "Rules of Procedure for Board of Directors Meetings". If a director has a personal interest in any meeting agenda item and such interest is likely to affect the Company's interests, the director is required to proactively disclose the nature of the conflict during the meeting and must abstain from both discussion and voting on the relevant resolution. In addition, the director may not act as a proxy to vote on behalf of other board members. The meeting minutes shall accurately document the directors' disclosures and recusals to ensure a fair and transparent decision-making process, thereby upholding the principles of sound corporate governance and business integrity. The Corporate Governance Officer is responsible for providing reminders and procedural support regarding conflict of interest avoidance during board operations, thereby reinforcing regulatory compliance and objectivity in decision-making. This ensures that the Board's overall operations align with the requirements of the "Corporate Governance Best Practice Principles". For details on the 2024 implementation of directors' recusals from proposals involving conflicts of interest, please refer to section "2.3.1 Operation of the Board of Directors" of the Company's Annual Report.
2.1.2. Functional Committees
To strengthen corporate governance operations and enhance professional oversight, Quanta has established functional committees under the authority of the Board of Directors, including the Audit Committee, the Remuneration Committee, and the Sustainability Steering Committee
- The Audit Committee, which assumes the responsibilities of the former Supervisors, is composed of three Independent Directors. The current (third) term commenced on June 17, 2022, in conjunction with the re-election of the Board of Directors. The committee members are Independent Directors Hung-Ching Lee, Pisin Chen, and Su- Pi Shen. Among them, Hung-Ching Lee and Su-Pi Shen possess expertise in finance or accounting. Hung-Ching Lee serves as the convener and chairperson of the committee meetings. The current term runs from June 17, 2022, to June 16, 2025, aligning with the term of the Board of Directors. For details on the committee's operations, please refer to section "2.3.2 Audit Committee Operations" of the Company's Annual Report.
- The Remuneration Committee operates in accordance with the "Remuneration Committee Organizational Charter". The term of office for committee members coincides with that of the Board of Directors that appointed them. The fifth-term committee consists of three members with a three-year term, from July 15, 2022, to June 16, 2025, aligning with the term of the current Board of Directors. Committee members are required to exercise the duty of care of a prudent manager and to faithfully perform their responsibilities, with their recommendations submitted to the Board of Directors for deliberation. For details on the committee's operations, please refer to section "2.3.4 Remuneration Committee Composition and Operations" of the Company's Annual Report.
- In December 2022, the Board of Directors approved the renaming of the former "Corporate Sustainability Development Committee" to the "Sustainability Steering Committee" and elevated its organizational status to report directly to the Board of Directors. The Sustainability Report is prepared annually, reviewed and approved by senior executives and the President, and then submitted to the Board of Directors for final approval. Once approved, the report is published in the "ESG" section of the Company's official website and disclosed on the Market Observation Post System (MOPS). In 2024, the Sustainability Steering Committee, together with its related subcommittees, convened a total of seven meetings. At the end of each fiscal year, the committee consolidates stakeholder identification and engagement results and reports them to the most recent Board meeting in the following year.
| Functional Committees | Member | Responsibilities | Attendance Rate | Resolutions in 2024 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Audit Committee |
Convener: Hung-Ching Lee (Independent Director) Committee Member: Pisin Chen (Independent Director) Committee Member: Su-Pi Shen (Independent Director) |
|
100% |
|
| Remuneration Committee |
Convener:
Hung-Ching Lee
(Independent Director) Committee Member: Samuel Lee (Designated Member) Committee Member: Su-Pi Shen (Independent Director) |
|
100% |
|
| Sustainability Steering Committee |
Chairman: Barry Lam Vice Chairman C. C. Leung Director: C. T. Huang Senior Executives |
|
100% |
|
2.1.3. Business Integrity
Quanta has established a comprehensive integrity governance framework based on the "Ethical Corporate Management Principles" and the "Integrity and Ethics Policy and Implementation Guidelines", which clearly define the ethical and compliance principles to be followed in all business activities. The company adopts a zero-tolerance policy toward any form of corruption, bribery, extortion, embezzlement, conflicts of interest, insider trading, and other improper conduct. Any violations will be subject to strict disciplinary actions in accordance with company regulations, and legal accountability will be pursued when necessary.
Quanta has established and announced multiple integrity-related management systems, serving as the core guidelines for the Company's business integrity operations. These include the "Corporate Governance Best Practice Principles" and the "Code of Ethical Conduct," both approved by the Board of Directors, which clearly define the behavioral standards and precautions to be followed in business operations. Additionally, to prevent insider trading, internal control systems such as the "Material Information Handling Procedures" and the "Insider Trading Prevention Procedures" have been established. In addition, the "Integrity and Ethics Policy and Implementation Guidelines" have been approved and announced by the President to further reinforce the Company's culture of integrity. To strengthen the integrity and ethical awareness of all employees, the Company has also established the "Code of Ethics and Business Conduct", which is regularly promoted and reviewed by relevant departments through annual training and system evaluations. The Business Integrity Policy encompasses multiple specific requirements, including prohibitions against offering or accepting any form of improper benefits (such as cash, gifts, travel, or promises of contractual employment), engaging in insider trading or unfair trade practices. The policy mandates compliance with antimoney laundering and counter-terrorism financing laws and requires avoidance of political donations or other financial activities that do not conform to regulations. As of the reporting period, the Company has made no political contributions or lobbying expenditure. Furthermore, the Company has established a comprehensive accounting system and internal control mechanisms and continuously reviews their effectiveness to ensure transparent information disclosure in compliance with regulations.
Integrity, Ethics, and Anti-Corruption Management Mechanism
Quanta is committed to upholding business integrity and anti-corruption governance by establishing a systematic, transparent, and responsive management framework. Through risk assessment, internal control systems, whistleblowing procedures, and feedback loops, the principle of business integrity is deeply embedded in all operational management processes. Corruption risk assessments have been completed across all operational sites, covering key functions such as procurement, finance, human resources, legal affairs, and manufacturing. The evaluation results are incorporated into the review of the management system and combined with internal control and audit processes to continuously improve risk response mechanisms, thereby enhancing overall governance effectiveness and organizational resilience. Integrity and anti-corruption management practices include:
- Regulatory Framework Design: Based on the "Ethical Corporate Management Principles", "Integrity and Ethics Policy and Implementation Guidelines", and "Insider Trading Prevention Procedures", the Company has established specific behavioral standards that prohibit bribery, acceptance of improper benefits, conflicts of interest, insider trading, money laundering, and anti-competitive conduct.
- Risk Management Integration: Integrity and anti-corruption issues are integrated into the Company's operational risk management process. These risks are continuously monitored and audited through annual audit programs and control measures.
- Reporting and Protection Mechanism: Multiple reporting channels are in place, with clearly defined principles of confidentiality and protection against retaliation to safeguard the rights of both internal and external whistleblowers, thereby fostering a culture of transparency and accountability.
- Continuous Review and Adjustment: Integrate internal feedback and practical implementation experience to regularly review management systems and training content, ensuring the effectiveness and timeliness of the systems.
Training and Awareness
Quanta continues to deepen all employees' understanding and practice of business integrity and anti-corruption through education and training as well as diverse promotional methods, thereby strengthening the concrete implementation of integrity principles in daily work. The purpose of the training is to establish correct value recognition, assist employees in identifying potential risks, avoid improper behavior, and strengthen understanding and trust in the Company's systems and reporting mechanisms. The relevant training covers fundamental concepts of business integrity, identification of improper benefits, anti-corruption behavior, declaration of conflicts of interest, prevention of insider trading, anti-competitive regulations, information confidentiality, and anti-money laundering measures. The training program primarily consists of orientation training for new employees and annual training for current staff. It is conducted through digital courses, presentations, case analyses, and interactive Q&A sessions to help employees gain a clearer understanding of the regulatory principles and behavioral standards.
In addition to training courses, Quanta also places great importance on the continuous promotion and reminders of the system. Each year, the Company promotes the reaffirmation of integrity-related policies among all employees through internal website announcements, employee newsletters, management meetings, and departmental communications. These efforts aim to enhance risk awareness and encourage the proactive reporting of suspicious activities. Relevant promotional information is also simultaneously announced on the Company's Integrity Communication Platform for all employees and stakeholders to access and use.
In 2024, the Company achieved the following results in business integrity and anti-corruption training and advocacy:
- Participation rate in business integrity and anti-corruption communications: 100%;
- Participation rate in business integrity and anti-corruption trainings: (including former employees).
- Coverage rate of integrity-related courses for new employees reached 100%;
- The annual employee conflict of interest declaration and awareness campaign completion rate was 100%.
Appeal Channels and Protection
Quanta encourages all employees to remain highly vigilant against any violations of the Code of Ethics and Business Conduct and emphasizes that each employee bears the responsibility to report any suspected misconduct when identified. In addition to reporting to their immediate supervisor, employees may also, depending on the circumstances, directly report to the Human Resources Director, the Internal Audit Unit, or submit a complaint through the employee grievance mechanism. Beyond internal reporting channels, Quanta has also established dedicated mechanisms for suppliers, customers, and other stakeholders to raise concerns or provide feedback. These channels are publicly available on the Company's official website and include:
- Corporate Social Responsibility Contact Point (CSR representatives at each manufacturing site)
- Professional Ethics Complaint Window (Independently established at Company Headquarters)
Complaints may be submitted either anonymously or with identification. If the case involves personnel at the governance level, it will be reported to the Chairman or Vice Chairman, who will assign a dedicated supervisor to conduct an independent investigation together with the audit personnel. For violations involving general staff, the Internal Audit Team will conduct the investigation and report the results to the highest executive of the General Management Office as the basis for further action. If the investigation confirms the misconduct, disciplinary measures will be taken in accordance with the Company's work regulations. In cases of serious violations, legal action will be pursued as necessary. For suppliers found to have breached the Code of Ethics and Business Conduct, the Company reserves the right to terminate the partnership in accordance with the contractual terms. To foster a safe and trustworthy environment for whistleblowing, Quanta is committed to maintaining strict confidentiality of all complaint-related information and the identities of complainants. The Company ensures that whistleblowers are protected from any form of retaliation, threat, or improper treatment. Major complaints related to integrity and the annual implementation status will be compiled and reported to the Board of Directors, explaining the investigation results and improvement measures, jointly promoting a healthier organizational culture and governance environment.
Quanta pledges that all employees and stakeholders who participate in the investigation process in good faith whistleblowing will be fully protected and will not suffer any form of retaliation, threats, or unfair treatment. The confidentiality of the whistleblowing information will be ensured throughout the entire process, establishing a trustworthy and effective integrity complaint mechanism.
| Number of Reported Ethical Conduct Violations/ Number of Substantiated Cases | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Substantiated Cases | Number of Substantiated Cases | Number of Substantiated Cases | Number of Reported Violations | Number of Substantiated Cases | ||
| Business Ethics and Operations | Corruption and Bribery | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Conflicts of interest | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Fair Competition | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Insider Trading | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Trade Secrets | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Privacy/Personal Information Protection | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Others (Political Donations, Charitable Contributions, and Social Participation) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Total Number of Cases Related to Business Ethics and Operations | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Human Rights Protection | Discrimination | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Harassment | 7 | 9 | 6 | 36 | 26 | |
| Occupational Health and Safety | 0 | 0 | 5 | 13 | 7 | |
| Total Number of Cases Related to Human Rights Protection | 0 | 0 | 5 | 13 | 7 | |
| Environmental Protection | Total Number of Cases Related to Environmental Protection | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 0 |
Note 1: Detailed information on reported incidents and substantiated cases is provided below:
2.1.4. Compliance with laws and regulations
Quanta recognizes that regulatory compliance is fundamental to sound business operations and integrity-driven governance. The Company remains firmly committed to the principles of legal compliance and ethical governance, actively reinforcing adherence to local laws, industry standards, and international conventions across its global operations. The Company has established a compliance management framework, coordinated by the Legal Department, which collaborates with various units to regularly identify regulatory changes and risks related to labor, environment, finance, anticorruption, fair trade, and personal data protection, ensuring that both policies and implementation measures remain aligned with legal requirements.
To enhance compliance awareness, the Company continuously conducts relevant training and promotional activities, covering topics such as business integrity, prevention of insider trading, ESG regulatory updates, and personal data protection. Additionally, legal updates are also consolidated into internal guidance materials to support employee understanding and adherence. The company has also established a dedicated whistleblowing system, providing stakeholders and employees with the means to report misconduct via telephone, email, or written communication. Details of the "Corporate Integrity Reporting System" and relevant contact information are publicly available on the Company's official website. All reported cases are investigated and handled by designated units, and when necessary, reported to the compliance supervisor or the Board of Directors. The rights of whistleblowers are protected, and retaliatory actions are strictly prohibited.
To enhance disclosure transparency, Quanta considers any single non-compliance incident with a fine imposed by the competent authority of NT$1,000,000 or more as a major non-compliance incident. In 2024, there were no records of material noncompliance with environmental, social, or economic-related laws, nor were there any legal proceedings involving anti-competitive, monopolistic, or antitrust behaviors. In the future, efforts will continue to strengthen risk warning and compliance mechanisms, enhancing the resilience of international legal compliance and the maturity of governance.
2.2 Risk Management
In the face of a highly volatile and uncertain operating environment, an effective risk management mechanism has become a critical element for the sound operations and sustainable development of enterprises. Quanta continues to strengthen its risk governance system by establishing a comprehensive risk management framework and operational procedures that encompass strategic planning, operational management, and regulatory compliance. Through institutionalized management and risk identification mechanisms, the Company ensures it has the capability for timely response and continuous improvement when facing potential risks, thereby enhancing overall resilience and operational efficiency.
2.2.1 Risk Governance
Risk Governance Framework and Management Scope
Risk governance serves as a fundamental framework for enterprises pursuing sustainable development. To mitigate the potential impact of risk events on corporate operations and to focus on business growth and improving operational efficiency, Quanta continues to develop and uphold a comprehensive risk management system. The Company's "Risk Management Guidelines" were approved by the Board of Directors in 2020 (policy link) to enhance overall risk control effectiveness and ensure that all types of operational risks are manageable and transparent.
To achieve the Group's overall risk governance objectives, Quanta has implemented a comprehensive risk management mechanism that covers all subsidiaries. This mechanism integrates principles of sustainable governance and the protection of stakeholders' rights and benefits, thereby establishing the Group's risk management framework. In line with risk management principles, Quanta has developed a formal risk governance organizational structure, centered around the "Three Lines of Defense" model, which serves as the core foundation for effective risk identification, control, and oversight.
Risk Governance Organizational Chart
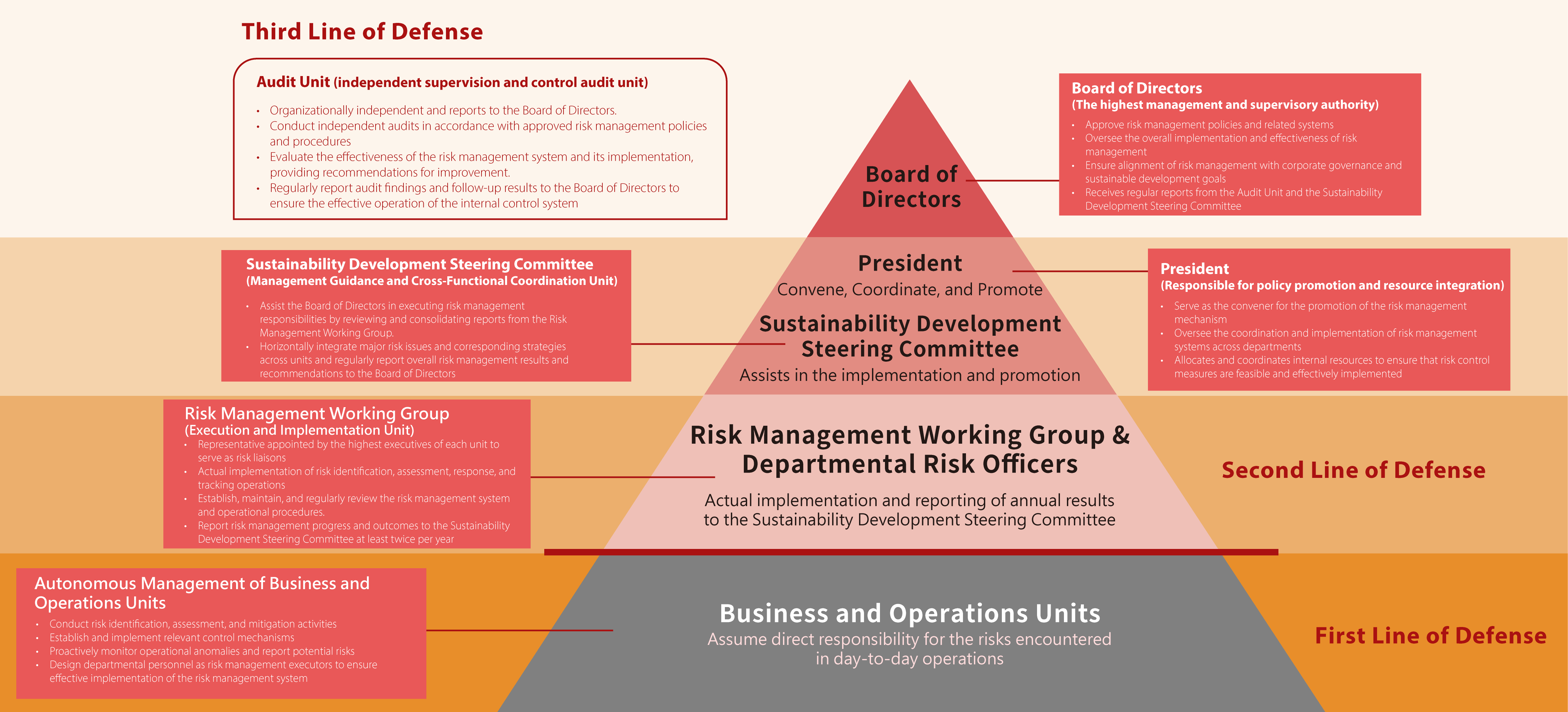
In response to the Financial Supervisory Commission's regulations, Quanta initiated the implementation plan for IFRS Sustainability Disclosure Standards by the end of 2024. This initiative aims to further clarify and strengthen the governance of sustainability-related risks, with progress and key execution items to be disclosed throughout the course of implementation. Among them, sustainability risks are assessed based on the IFRS S1 and S2 sustainability disclosure standards, integrating environmental, social, and governance (E, S, G) related risks and opportunities with financial evaluation. These risks are reported to the Board of Directors through a specific reporting mechanism to ensure effective reflection in operational strategies or financial governance.
Risk Management Process and Implementation
Quanta's risk management process primarily encompasses four core steps: risk identification, risk assessment, risk response, and execution with risk monitoring. This framework establishes a sustainable risk management system equipped with early warning capabilities and a dynamic adjustment mechanism. The overall process design is based on annual operational experience, internal expert opinions, external industry risk reports, and benchmarking against peers, with a rolling update of key assessment points and management strategies. To ensure alignment with the Company's sustainable operation and risk governance objectives, Quanta also incorporates major risk topics such as emerging technologies, climate change, social changes, and global geopolitical issues into its considerations, comprehensively assessing their potential impacts on operational opportunities and financial stability.
To further enhance the maturity of risk governance, Quanta is actively promoting the establishment of a Risk Appetite framework to serve as the foundation for risk identification, measurement, and response. The risk appetite will encompass aspects such as financial, operational, regulatory compliance, information security, and ESG. It will be defined using quantitative indicators (such as financial impact) and qualitative criteria (such as reputational damage and compliance risk). Recommendations will be proposed by senior management, discussed by the Risk Management Working Group and the Sustainability Development Steering Committee, and then submitted to the Board of Directors for approval. The risk appetite will be regularly reviewed and revised according to changes in internal and external circumstances to ensure that the Company maintains robust risk control and sustainable operational capabilities while pursuing growth and innovation.
Annual Update and Rolling Review
| Risk Identification |
|
| Risk Assessment |
|
| Formulation of Response Strategies |
|
| Execution and Monitoring |
|
Risk Reporting Mechanism
Quanta places strong emphasis on the connection between stakeholders and risk governance. Through formal disclosure channels-such as the Annual Report, Sustainability Report, and designated stakeholder contact points, the Company communicates its risk governance outcomes. These results are made publicly available via official reports and website announcements, ensuring that external stakeholders can access and understand the effectiveness and progress of Quanta's risk management efforts. In addition, transparent information disclosure and feedback mechanisms are in place to support stakeholder participation in the risk governance process, enabling them to raise concerns and express opinions.
Recent Implementation Status for the Past Two Years
2023 Risk Assessment Results
In 2023, Quanta's risk assessment covered four major sites: QCI, QSMC, QCMC, and QMB. A total of 4 high-risk, 9 medium-risk, and 65 low-risk items were identified. Corresponding contingency plans were developed for all high-risk items to strengthen risk resilience and response capabilities, serving as an important basis for formulating next year's risk responses and strategies. The relevant risk management performance was formally reported on December 20, 2023, in order to continuously enhance the Group's sustainable risk management mechanism.
2023 High-Risk Items and Contingency Plans
| Risk Theme | Risk Description | Contingency Plan | 2024 Implementation Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Consumption and GHG Emissions | Organizational GHG Inventory Management System: The established platform system still requires optimization and cannot yet fully and effectively control and calculate GHG emissions. This could hinder compliance with the committed Science-Based Targets (SBTs), fail to meet customer expectations, and potentially lead to additional costs. | GHG inventory management and consolidation | Completed GHG inventory in line with financial boundaries, as well as internal system and form audits; established a blueprint for the inventory system. |
| Product Carbon Footprint Management System: The sustainability-related database requires further optimization and enhancement. For example, carbon footprint calculation accuracy remains limited, which may fail to meet customer expectations and could lead to loss of orders. | Product carbon footprint management and mechanism development | Established the basic framework for Quanta's product carbon footprint calculations and built a management system; completed initial training. Planned internal system and product carbon footprint system optimization and automated calculation process improvements. | |
| Supplier Management | The scope of supplier due diligence is limited, making it difficult to fully anticipate potential supply chain risks and assess their impact, which could result in supply chain disruptions. | Sustainable supplier management and due diligence mechanism development | Completed relevant assessment and investigation form planning and development; planned the development of a sustainable supplier management system. |
| Risk Assessment and Risk Management | The scope of the Group's risk assessment is limited, leaving the company exposed to risks that may not be managed appropriately. | Corporate risk management mechanism development | Completed relevant assessment and investigation form planning and development; expanded the scope to cover more sites. |
Based on the 2023 risk assessment results, Quanta identified multiple high-risk issues, reflecting the high expectations from both the operating environment and stakeholders for sustainable performance. To proactively address these challenges, Quanta proposed six major management guidelines in 2023, serving as the core direction for driving risk prevention, management, and transformation strategies, successfully laying the foundation for a forward-looking sustainability blueprint. Below are the concrete performance results for 2024.
- Strengthening Employee Sustainability Awareness
- In response to ESG evaluation requirements from high-standard customers such as in the automotive and server sectors, promoted sustainability training covering environmental, governance, and social dimensions.
- Enhanced employee understanding of corporate sustainability goals and ESG evaluation contents, embedding a sustainability culture into daily operations and across all functional organizations.
-
Establishing a Sustainable Risk Management Framework
- Addressed global geopolitical, inflationary, energy crisis, and supply chain risks by strengthening corporate risk management strategies.
- Systematically identified and controlled risks in governance, strategy, operations, compliance, and finance, building a resilient risk control system.
- Improved Business Continuity Planning (BCP) capabilities for both the company and the supply chain.
- Continued to optimize the sustainability management organizational structure in 2024, promoting Quanta's sustainability process in a more systematic and efficient manner.
-
Driving Low-Carbon Innovation and Green Design
- Completed the product carbon footprint platform and initiated the sustainable supplier management system project to promote comprehensive environmental and social responsibility management in the supply chain.
- In line with Science-Based Targets (SBTs) and key customer requirements, it promoted low-carbon transformation in product design, manufacturing processes, material selection, and supply chain management.
- Integrated innovative R&D with green design concepts to enhance the company's competitive advantage under sustainability transformation and net-zero goals.
-
Fostering Talent Sustainability
- Following international evaluation indicators such as DJSI and MSCI, identified talent-related risks and proposed strategies for strengthening human capital management and development.
- Focused on talent structure, demographic risk assessment, incentive mechanisms, and enhancing organizational competitiveness to ensure sustainable talent momentum for the enterprise.
-
Aligning with International Standards and Guiding Supply Chain Sustainability Due Diligence
- Implemented responsible sourcing practices by conducting due diligence on suppliers' operations, human rights, materials, and environmental aspects, in accordance with key customer requirements.
- Enhanced supply chain sustainability governance and overall resilience through risk identification and management.
-
Practicing Social Care and Public Engagement
- Actively participated in various public welfare activities and continued to invest resources in caring for disadvantaged groups.
- Fulfilled corporate social responsibility through diverse social engagement, promoting mutual benefit and amplifying positive impact.
2024 Risk Assessment Results
Meanwhile, Quanta's 2024 risk assessment covered six major sites-QCI, QSMC, QCMC, QMB, QMH, and QMMC-identifying a total of 8 high-risk, 10 medium-risk, and 63 low-risk items. Corresponding contingency plans have been formulated for all high-risk items, serving as an important basis for next year's risk response and strategy planning. Quanta will continue to optimize its risk management framework and gradually expand the scope of risk assessments to cover all Group operating sites, with the goal of establishing a comprehensive risk identification and control mechanism. The relevant risk management performance was formally reported on December 27, 2024.
High-Risk Items and Risk Contingency Projects for the Current Year
| Risk Theme | Risk Description | Risk Contingency Plan Items |
|---|---|---|
| Talent Attraction and Retention | Loss of managerial talent and insufficient mid-level leadership are affecting the overall execution of organizational strategies and employee trust. | Establishment of a Sustainable Talent System |
| Talent Development | The organization lacks appropriate training programs or career development pathways, resulting in employees' skills not being effectively enhanced to support long-term growth. | |
| Energy Consumption and GHG Emissions | Organizational GHG Inventory Management System: The existing management system requires optimization. Incomplete emission control and calculation hinder compliance with SBT targets and customer expectations, possibly leading to increased costs. | Sustainable Information Management Digitalization & Automation Internal System Optimization |
| Product Carbon Emission Management System: The sustainability-related database remains underdeveloped, with limited accuracy in carbon footprint calculations. This shortfall may lead to failure in meeting customer expectations and potential order losses. | ||
| Supplier Management | The scope of due diligence conducted on suppliers is limited, resulting in an incomplete assessment of the likelihood and impact of supply chain risks, which may pose a risk of supply chain disruption. | |
| Management Duties and Responsibilities | The Sustainability Task Force has not yet been fully established or developed. Additionally, the connection between sustainability performance and both senior management and general staff is weak, hindering internal implementation and promotion efforts. | Establishment of a Mechanism Linking Sustainability Indicators with Individual Performance |
| Risk Assessment and Risk Management | The scope of the Group's risk assessment is limited, exposing the Company to risks that may not be managed appropriately. | Expansion and Enhancement of Corporate Risk Management Scope |
| Improvement Objectives | Lack of annual and short-, medium-, and long-term CSR/ESG goals, making it difficult to track continuous improvement efforts. | Establishment of a Sustainable Strategy Indicator Target System |
In response to the results of the 2024 risk assessment, Quanta identified eight high-risk issues spanning talent sustainability, carbon management, supply chain governance, and internal management mechanisms. These findings indicate that there remains room for improvement in areas such as talent development, climate action, and organizational resilience. To strengthen risk response capabilities and enhance overall sustainability performance, Quanta has formulated specific contingency plans based on the assessment results and, accordingly, established six key operational management guidelines for 2025. These guidelines focus on risk prevention, organizational capacity building, and information governance upgrades, with the aim of advancing sustainability governance strategies and building a more resilient, value-driven business model.
- Leverage Committee Functions to Drive Achievement of Sustainability
Targets
- Establish short-, medium-, and long-term ESG goals aligned with international ESG indices (DJSI, MSCI, etc.) and IFRS disclosure standards.
- Integrate sustainability indicators into the performance appraisal system to improve external transparency and internal execution.
- Embed sustainability principles into business management and core employee values to deepen the sustainability culture.
- Enhance Corporate Sustainability Risk Management Framework and Implementation
- Build a risk identification and response mechanism covering environmental, social, and governance (ESG) dimensions.
- Address complex risks such as geopolitical tensions, inflation, and energy challenges.
- Establish Business Continuity Plans (BCP) to strengthen supply chain resilience and internal risk control.
- Advance Talent Sustainability to Enhance Corporate Competitiveness
- Strengthen human resource management by introducing diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) and Taskforce on Inequality-related Financial Disclosures (TIFD) indicators.
- Develop recruitment and retention strategies while promoting sustainabilityoriented training and employee well-being systems.
- Transform the sustainability culture into an Employee Value Proposition (EVP) to deepen organizational identification.
- Pursue Net-Zero Emissions Through Energy Saving, Carbon Reduction, and
Low-Carbon Innovation
- Obtain Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi) verification and initiate carbon reduction actions and transition plans.
- Implement concrete measures in low-carbon design, supplier carbon management, and process improvements.
- Use carbon reduction as a driver for innovation, enhancing sustainability performance across the entire value chain and supply chain.
- Promote Sustainable Supply Chain Management and Expand Due Diligence
Scope
- Require suppliers to conduct due diligence on human rights, environmental, and material-related aspects.
- Introduce digital platforms to enhance supplier ESG information disclosure and governance mechanisms.
- Build a resilient sustainable supply chain to meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- Digitalize and Optimize Sustainability Information Management Systems
- Develop an integrated data platform to improve data collection and analysis efficiency.
- Strengthen ESG indicator tracking and decision-making support to improve the quality of both internal and external disclosures.
- Foster collaboration and transparency across the value chain to enhance corporate sustainability competitiveness.
2.2.2 Management of information security
Information security is a crucial cornerstone for sustainable development and maintaining core competitiveness in the enterprise. At Quanta, we are committed to enhancing the overall management of information security as our goal. We have established a layered defense framework to enhance overall protection and conduct comprehensive risk monitoring. We will continue to refer to domestic and international trends, international standards, and advice from external professional consultants to allocate appropriate security budgets annually, optimize various protective control measures, strengthen education and training for all personnel, improve security awareness and response capabilities, and safeguard the Company's operations and information security.
Quanta's Information Security Strategy: "Everyone participates, controls risks, and ensures the effective operation of the information security system to protect the normal operation of the Company".
Quanta's information security policy has three objectives: "Everyone participates and controls risks", "actively prevents, continually improves", and " client trust, sustainable operation":
- Everyone participates and controls risks: Establishing an information security management system, determining the functions and responsibilities of information security, and managing information security comprehensively across all processes and staff. According to the characteristics of the Company's information security, the requirements of laws and regulations, the risk assessment procedures are established, and the risk acceptance criteria are determined. Conducting regular risk assessment and taking appropriate measures to reduce potential risks.
- Actively prevents, continually improves: In business operations, emphasis is placed on information security, identifying and analyzing weaknesses and potential threats in information systems, considering the balance of costs, benefits, and risks, classifying and protecting assets, and protecting information systems at an appropriate cost.
- Client trust, sustainable operation: By conducting performance evaluations and continuous improvement, we ensure the effectiveness of the information security management system and achieve the goals of client trust and sustainable business operation.
Information Security Management Organizational Structure
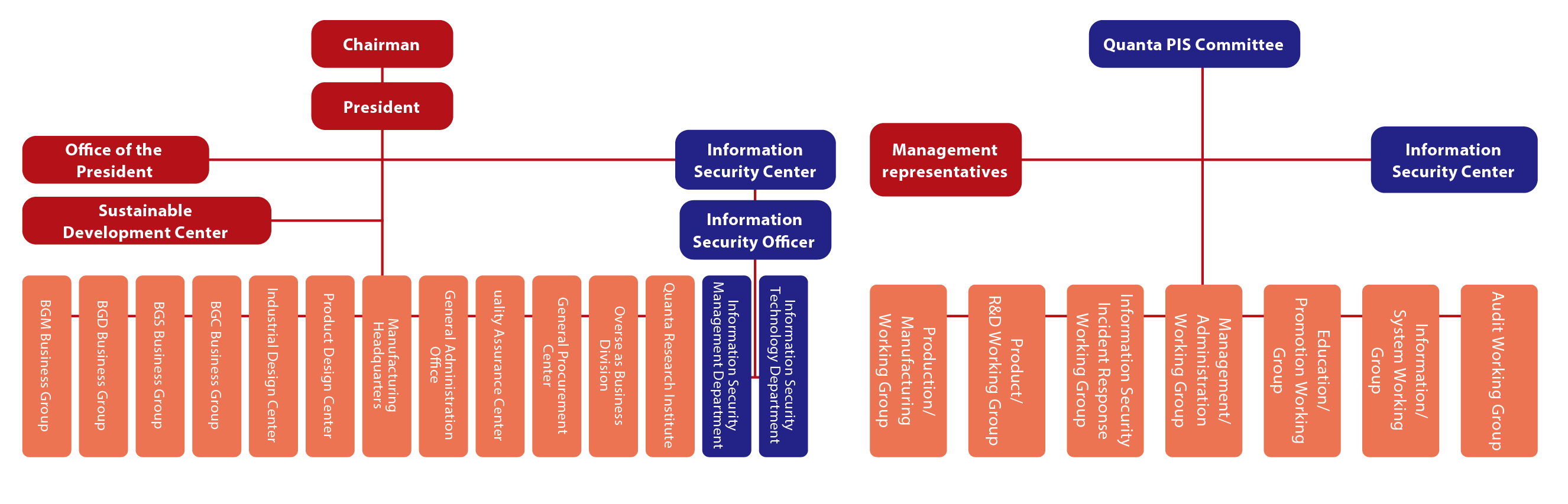
In 2022, Quanta passed a resolution through the Board of Directors to establish a dedicated information security unit and appoint an Information Security Officer. The Information Security Officer is served by the Vice President of the Management Information Center. The information security unit is called the "Information Security Center" and reports directly to the President or his designated representative. It is responsible for convening meetings of the Proprietary Information Security Committee (PIS). The "Information Security Center" has set up the "Information Security Management Department" and the "Information Security Technology Department", responsible for the management of information security matters within the group. This includes coordinating information security policies, international information security standards verification and auditing, implementing and verifying information security mechanisms, building layered defenses, enhancing information security levels, and aligning with international standards. The center regularly reports on relevant risks, issues, and management effectiveness. The organizational structure of information security management is illustrated in the diagram below.
To demonstrate the Company's good information security management and strengthen cross-departmental collaboration within the group, the PIS committee is the highest guidance unit for group-wide information security. Through biannual committee meetings, monthly meetings of the Information Security Center, and regular and ad hoc project meetings, various information security management policies and measures are continuously promoted. Comprehensive reviews and optimizations of information security policies and measures are conducted at least once a year, and the execution of information security is reported to the Board of Directors at least once a year. The most recent report was submitted on December 27, 2024.
Status of Information Security Management Implementation
Quanta has established four dimensions of information security governance to achieve its vision and goals: strengthening overall response capabilities, establishing an information security defense framework, enhancing information security protection systems, and advancing autonomous information security capabilities. In response to the increasing security risks, Quanta continuously adjusts its information security direction based on risk management results, as well as the development of information and communication technology and external environmental changes. Quanta aims to establish consistent security standards throughout the Group, strike a balance between business and security, and ensure that all employees actively participate in collaborative maintenance to meet the Company's security policy requirements. In order to evaluate the performance and effectiveness of the information security management system, the Company has established several KPIs for the organization, personnel, processes, and technical aspects of information security, strictly examining the implementation of the information security management. All KPIs were controlled, improved and successfully achieved in 2024. The relevant KPIs are shown in the table below.
Constructing an Overall Information Security Framework
Quanta places great importance on information security. Since 2008, the Company has maintained information security insurance and, in 2009, formulated the "Information Security Management Policy" and "Information Security Risk Management Framework." Beginning in 2020, Quanta initiated planning for ISO 27001 certification, actively advanced implementation in 2021, and successfully obtained certification in the second quarter of 2022. In the third quarter of 2024, Quanta completed the transition to ISO 27001:2022 and expanded the certification scope-covering all information systems and increasing the number of certified personnel by 2.5 times-to meet rising information security demands. Currently, three sites-QCI, QSMC, and QQCMC-have obtained ISO 27001 certification. The Company plans to certify two additional sites by 2025 and one more site by 2026, continuing its efforts to implement a comprehensive information security management system across all global locations.
With rapid technological development and growing reliance on digital tools, information security has become a key issue for business continuity. Even minor vulnerabilities can result in significant operational disruptions. Quanta recognizes the need for evolving cybersecurity mechanisms to counter increasingly sophisticated cyber threats. To this end, the Company has established a comprehensive defense mechanism, encompassing both regular and ad hoc risk assessments, threat and vulnerability scans, corresponding control measures, and real-time detection and protection systems. This approach ensures timely identification, control, and mitigation of high-risk issues. All high-risk information security items identified in 2024 have been successfully addressed and strengthened according to the planned corrective actions.
To address supplier-related risks, Quanta conducts necessary risk assessments based on suppliers' level of access to the Company's information and communication technology environment and the services provided-such as information services, hardware, system construction and maintenance, and cloud services. Suppliers are required to sign information security confidentiality agreements and security acknowledgment forms aligned with the respective security requirements. In addition, Quanta performs annual monitoring and reviews of information hardware and service vendors. If a supplier's evaluation score falls below the acceptable threshold, an online or on-site audit is initiated. Suppliers who fail the audit and are unable to implement corrective actions will have their supplier status revoked. In 2024, a total of 18 suppliers were assessed, all of whom met the qualifying standards.
| Aspects | Information Security KPI | Handling status in 2022 | Handling status in 2023 | Handling status in 2024 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organization | Review of Management System Documents | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Risk Assessment Operations | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Personnel | Confidentiality Agreement Signing | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Information Security Education and Training | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Technology | Audit Record Management | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Vulnerability Scanning Management | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Appropriateness of Firewall Rules | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Core Server Availability Rate | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Server Room Infrastructure Availability Rate | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| External Network Availability Rate | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Process | Formal Environment Access Management | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Software Legal Authorization | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Application System Change Authorization | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Information Security Incident Reporting Time | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Operational Continuity Drill Procedures | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Authorization and Record of Access to the Server Room | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| System Security Related Settings | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Furthermore, to stay abreast of the latest threat intelligence and information security incident investigation techniques, Quanta actively participates in both domestic and international information security response organizations. The Company continues to deepen its information security defense capabilities, optimize protective measures, promote a Zero Trust Architecture, and leverage information security AI technologies to strengthen protection intensity and enable comprehensive, real-time monitoring. Rigorous risk assessment and control procedures are implemented, and dedicated information security budgets are allocated annually to reinforce information and communication technology security safeguards. Regarding the handling of informaiton security incidents, Quanta has implemented a information security incident response procedure and established an incident management process plan. The Company conducts annual internal drills and coordinates with clients to carry out information security incident reporting, response, and business continuity exercises. Furthermore, Quanta ensures the enforcement of information security incident reporting and the disclosure requirements for significant information security information.
Quanta also regularly conducts self-assessments and improvement activities in accordance with the "Guidelines for Information Security Control of Listed and OTC Companies" and implements a personal data protection system to comply with relevant information security and personal data protection regulations. Quanta places great importance on information security issues of concern to all stakeholders. By integrating the Company's sustainable development and information security policies, it provides open and transparent information security management information, establishes effective communication channels with stakeholders, and responds to their expectations. The Company's main information security operations are as follows:
| Aspects | Key Projects | Main Operations |
|---|---|---|
| Organization | Strengthening the Functions of the PIS Committee | The PIS Committee serves as the highest governing unit for information security within the group. Through biannual committee meetings, it continuously promotes various information security management policies and measures, integrates the Group's information security management audits, and facilitates a cross-functional committee horizontal communication mechanism. |
| Group Information Security Centralized Management | The dedicated information security unit is the Information Security Center, which comprises the Information Security Management Department and the Information Security Technology Department, responsible for managing the Group's information security affairs. To continuously promote information security efforts across all sites, dedicated information security personnel have been assigned at each location to implement information security measures locally and ensure compliance with the Group's information security standards. | |
| Promoting Information Security Risk Defenses | Promoting the Information Security Risk Management Defense : Units conduct self-inspection and supervision through information security supervisors/ representatives, while dedicated information security units serve as the second line of defense. This is complemented by a comprehensive internal control system to identify, assess, and manage high-risk information security operations across various business activities. | |
| Integrating Accident Response Resources | Integrate the information security capabilities of the headquarters and various branches to establish a group information security incident response team. Participate in organizations such as TWCERT/TW-ISAC, SP-ISAC, and FIRST to promptly monitor domestic and international information security trends, incidents, and threat intelligence, and respond in a timely manner. | |
| Personnel | Fostering Quanta's Information Security Culture | Enhance the information security organization, establish multi-layered information security defense technologies, optimize information security management processes, and cultivate high-quality information security personnel. Through a variety of activities, Quanta fosters a strong information security work environment and a steadfast commitment to information protection, continually earning client trust. |
| Enhancing Autonomous Information Security Capabilities | Conduct professional competency analysis to identify staffing needs, inventory existing skills, and validate information security capabilities. Consolidate the essential self-competencies for information security personnel and develop and promote a information security competency training blueprint. | |
| Training Experts in the Field of Information Security | Based on the required competencies for information security professionals, Quanta continuously offers specialized training programs, encourages professional certification, and incorporates cross-disciplinary expertise. The Company also strengthens collaboration between industry and academia to cultivate information security experts within the organization. | |
| Improve Security Awareness and Recognition | Information security is a mandatory course for all employees every year, and passing a test is required. Annual PIS campaigns promote the five key principles of data protection, and social engineering drills are conducted to enhance employee awareness and understanding of information security risks. | |
| Technology | Implementation of Zero Trust Architecture | Building upon a multi-layered defense framework, Quanta has implemented a Zero Trust Architecture through a three-phase approach―identity authentication, device authentication, and trust inference mechanisms. This ensures tiered security protections across endpoints, networks, and application layers, continuously improving the maturity level of the Company's information security posture. |
| Client and Product Information Security Requirements | From the planning stage, information security collaboration is incorporated, with information security requirements integrated into specialized environments as requested by clients. Quanta also conducts real-time monitoring of product and ICT equipment vulnerabilities and threat intelligence to proactively identify and resolve security issues. | |
| Group Information Security Assessment | System security testing tools have been deployed to perform information security assessments and monitoring from both internal and external perspectives. These tools assist in identifying and mitigating security risks, with the implementation scope extended to all operational sites across the Group. | |
| Utilization of AI in Information Security | Advanced AI technologies are applied to information security protection processes for rapid detection, in-depth investigation, and accurate response. These capabilities shorten incident response and investigation times, help identify potential data leakage risks, and strengthen the Company's overall multi-layered defense system. | |
| Process | Establishing a Unified Information Security Standard for the Group | Quanta develops management policies in accordance with established standards, adheres to these policies, and implements risk control measures. The Company continuously drives improvements and is committed to expanding the scope of its certifications. By implementing information security management systems at each site, Quanta aims to establish a unified and consistent information security standard across the Group. |
| Implementation of Personal Data Protection System | A personal data protection system has been implemented through comprehensive data inventory and process analysis, integrated with the existing information security management system framework. This approach enhances Quanta's capabilities in safeguarding personal data throughout its lifecycle―from collection and processing to storage and usage―while ensuring compliance with applicable laws, regulations, and international best practices. | |
| Group Operation Site Information Security Audit | To maintain consistent safety standards throughout the organization, we conduct an annual information security audit at both domestic and international operational sites. The audit encompasses office environments, research and development facilities, and production manufacturing environments. Its objective is to ensure compliance with information security regulations and promptly identify areas for improvement. | |
| Group Information Security Risk Management | To monitor the current information security risk landscape within the organization, Quanta continues to develop an integrated information security standards and risk response management platform, complemented by visual tools such as dashboards. This framework enables real-time visibility into enterprise-wide information security risks and facilitates timely implementation of risk mitigation measures. |
Results of Information Security Control Execution
The Company conducts regular internal and external information security audits and client audits, and no major deficiencies or incidents that caused client or company losses have been found. We are able to respond to and control internal and external information security threats through various control measures.

Confidential Information Protection Policy
To safeguard the confidential information of the Company and its clients, Quanta has established a comprehensive information security management system and defense mechanisms. Additionally, the Company has implemented an extensive confidential information protection policy covering sensitive data such as intellectual property rights, personal privacy, and company operational information. The Company has established the "Patent Rights Management Measures", "Integrity and Ethics Policy", "Privacy Protection Management Procedures", "Quanta Computer Personal Data Protection Measures", and various manufacturing sites safety management regulations. Additionally, it promotes the "Five No's" action guidelines for protecting confidential information, thereby institutionalizing the implementation of confidentiality requirements. All new employees are required to sign a confidentiality agreement upon reporting for duty. Employees and suppliers involved in confidential projects must also sign confidentiality agreements to enhance the overall awareness of confidentiality and legal responsibilities among all personnel. This ensures that the Company's confidential information is not disclosed and that personal data is preserved and used in accordance with the law.
The PIS Committee is responsible for coordinating and promoting policies related to confidential information protection and regularly reviews the appropriateness of these management systems through scheduled meetings. Quanta undergoes irregular client audits to ensure the effective implementation of its information protection mechanisms.
Quanta has established a clear grievance and management mechanism. Employees who become aware of potential risks to confidential information may report through the Company's independent "Ethical Conduct Grievance Channel" (grievance link), or via their supervisors or the Human Resources Department. Upon verification, the responsible unit will promptly handle the matter, and if the issue is substantiated, disciplinary actions will be taken in accordance with the Company's Work Regulations. To further strengthen internal awareness and education, The Headquarter held 8 promotional sessions in 2024. The annual training program focused on enhancing information security protection measures and achieved a 100% participation and completion rate. The promotional sessions and training initiatives are expected to be expanded to major manufacturing sites within the next two years.
The implementation status over 2023 and 2024 is as follows:
- No client complaints related to privacy violations, personal data breaches, or breaches of confidentiality obligations were received in 2023 and 2024.
- All personal data were properly stored and utilized in accordance with applicable management policies, with no incidents of non-compliance reported.
2.2.3 Intellectual Property Management
Intellectual property Intellectual property is one of the key outputs of technological research and development, and research and development serve as the cornerstone for enterprises to achieve their strategic business objectives. Quanta places great importance on intellectual property. While protecting and managing its own intellectual property, it also respects the intellectual property of external partners, including customers, suppliers, and academic and research institutions, to prevent any infringement. Accordingly, Quanta has formulated a business management model that integrates commercial, R&D, and intellectual property strategies. This creates a continuous positive cycle aimed at enhancing corporate value, strengthening organizational resilience, ensuring operational autonomy, increasing industry competitiveness, and improving profitability.
In alignment with the Company's operational model, current intellectual propertyrelated matters primarily focus on patents, followed by trademarks. The primary method of acquisition is through in-house development, complemented by collaboration with academic and research institutions. Joint development is conducted on technologies with promising prospects through industry-academia cooperation projects. Additionally, some technologies are legally licensed from external sources based on operational needs. The Company has established an Intellectual Property Group to manage and utilize patents, trademarks, and other intellectual properties, conducting ongoing control to reduce the risk of infringement.
To strengthen the intellectual property management mechanism and encourage innovative research and development, Quanta has implemented the "Patent Rights Management Measures" since January 11, 2002, which were approved by the Chairman, serving as the policy basis and procedural guidelines for patent management. The Measures clearly outline procedures for patent proposal, filing, acquisition, and ongoing maintenance. In addition, the Company has established an incentive mechanism to reward employees for submitting patent applications, securing patent rights, and participating in the annual patent competition. These efforts aim to stimulate R&D momentum among employees and enhance the Company's overall technological competitiveness. The Company has published the "Patent Rights Management Measures" and the "Patent Proposal Application Form" along with other related documents on the internal website to ensure employees can access them in a timely manner, promoting transparency of the system and internal participation, thereby strengthening the institutionalization and operational efficiency of intellectual property management.
The Company has established a comprehensive patent application process and incentive system, which are incorporated into the "Patent Rights Management Measures" as the basis for internal implementation. Patent proposals are initiated by R&D personnel and undergo internal technical searches and patentability evaluations. Upon sequential approvals by the department head and the Vice President of the business unit, the proposals enter the formal application process. This ensures that technological innovations demonstrate originality, patentability, and commercial value. Simultaneously, a patent database system has been established to support intellectual property management. Based on departmental or individual access privileges, the system provides historical patent lists, statistical reports, and related information upon request. This enhances the transparency and operational effectiveness of intellectual property oversight. Additionally, quarterly patent reports are regularly published on the internal website to assist all colleagues in tracking the accumulation of R&D achievements and the progress of patent portfolio deployment.
To encourage employees to engage in innovation and research and development related to their duties, the Company has stipulated several incentive measures in the "Patent Rights Management Measures". Employees who complete a patent application or officially obtain a patent certificate will be notified along with their immediate supervisors. In accordance with the regulations, they will receive application and certification bonuses. Additionally, an annual patent innovation competition is regularly held, selecting the Technology Innovation Award from the patents granted in that year, with trophies and cash prizes awarded in recognition of their achievements. Simultaneously, the Company tracks the number of invention patents granted to R&D personnel each year. The employee with the highest accumulated score is awarded the "Annual Excellence in Innovation Award". This structured approach promotes continuous innovation and supports the growth of technological assets.
Intellectual Property Management System, Application Strategies, and Protection Effectiveness
To strengthen the subsequent maintenance and strategic utilization of intellectual property rights, the Company has established a patent reexamination and review mechanism to ensure that patent interests align with technological progress and market trends. For patents nearing expiration, the Company initiates a review process one to three months prior to the expiration date. This involves joint discussions between the technical teams and original inventors regarding the patented technology, the current status of related products, and future market potential. A cost-benefit assessment of continued maintenance is conducted to determine whether to renew, abandon, or transfer the technology, thereby ensuring efficient resource allocation and maximizing the value of the patent portfolio.
At the operational level, the Company has established structured procedures for applying and approving external patent licensing and cross-licensing arrangements. Any authorization involving third-party use of patents owned by the Company must undergo internal evaluation and be approved by the President before proceeding. Such licensing arrangements not only extend the value of the Company's technological applications but also serve as strategic leverage in cross-licensing during external patent negotiations and cooperation discussions, thereby enhancing the Company's influence and flexibility in technology collaboration and industry chain negotiations.
The standard operating procedure for handling patent disputes is as follows:
- Upon receiving direct or indirect notifications of infringement disputes, the Business Division promptly informs the Legal Affairs Team and the Intellectual Property Team for handling.
- The Legal Affairs Team collaborates with relevant personnel from the Business Division to identify the parties involved and clarify their relationships based on the content of the notice. Concurrently, the IP Team conducts a technical analysis of the patents in question and works with the Business Division to determine the linkage between the disputed patents and the associated products or components.
- Based on the joint assessment by the Business Division, Legal Affairs Team, and IP Team, a response strategy is formulated. The Business Division and/or Legal Affairs Team then respond to the opposing party or affected customers accordingly.
- Further responses are managed in a timely manner by the Business Division and Legal Affairs Team, depending on the progression of the case.
To safeguard the Company's interests, the following measures to protect intellectual property rights are also implemented in daily operational processes:
- The confidentiality and intellectual property ownership agreements for outsourced operations, as well as measures to reduce the risk of infringement of procured products, are regulated through the signing of contracts/agreements by the business units in collaboration with the Legal Affairs Team colleagues. The review of contract intellectual property clauses is conducted collaboratively by the business unit and colleagues from the Legal Affairs Team.
- The confidentiality and intellectual property ownership agreements for research and development in collaboration with external organizations are formulated and regulated through contracts/agreements jointly drafted and signed by the business unit in coordination with the Legal Affairs Team and the external collaborating organizations. The acquisition and maintenance of intellectual property shall be executed by the Intellectual Property Team in accordance with contracts and agreements.
- Intellectual property (IP) agreements covering employee onboarding, employment, and termination are communicated during employee training sessions and clearly stated in the Company's work regulations. Upon signing, these agreements are centrally archived and managed by the Talent Resources Center.
- Measures for confidential control include conducting regular internal training on the Proprietary Information Security (PIS) control regulations and continuously implementing various promotional activities.
As of the end of 2024, Quanta has filed a cumulative total of 8,721 patent applications across Taiwan, the United States, China, Japan, and Europe, with 6,737 patents successfully granted. These achievements reflect the Company's sustained commitment to global intellectual property deployment and deep investment in technological advancement. In 2024, a total of 202 newly approved invention patents were added, covering areas such as information and communication technology, process optimization, and system integration. Additionally, 32 patents related to ESG sustainability issues were also applied for, demonstrating the Company's proactive integration of research and development innovation with sustainable development, strengthening technological advantages and supporting long-term carbon reduction and resource efficiency strategies.
2.3 Economic Performance
Quanta adheres to a strategic approach that balances sound management with innovation-driven growth. The Company continuously strengthens its core technological capabilities and global manufacturing footprint. Despite the volatile international environment and industry challenges, Quanta consistently demonstrates outstanding operational resilience and growth momentum. Guided by a long-term value orientation, the Company achieves dual progress in financial performance and sustainability goals through optimal resource allocation and improved operational efficiency, thereby creating shared outcomes for shareholders, employees, and society as a whole.
2.3.1 Financial Performance
In 2024, benefiting from the expansion of global AI data center infrastructure, the server business experienced leapfrog growth of more than double; meanwhile, the annual shipment volume of notebooks reached 45.9 million units, representing a 2.1% decline compared to 2023. The consolidated net revenue for the full year reached NT$1.41 trillion, up 30% from NT$1.09 trillion in the previous year. Additionally, in 2024, the gross profit margin, operating profit margin, and net profit margin were 7.9%, 4.4%, and 4.2%, respectively. Compared to the 2023 figures of 7.8%, 4.0%, and 3.7%, this represents another year of simultaneous improvement across all three margins.
The annual gross operating profit surpassed the NT$100 billion threshold for the first time, reaching NT$110.76 billion, representing a 30.5% increase compared to NT$84.89 billion in the previous year. The net profit after tax for the past two years was NT$60.28 billion and NT$40.49 billion, respectively, with net income attributable to the parent company's owners amounting to NT$59.70 billion and NT$39.68 billion, reflecting a year-on-year growth of 50.5%. In terms of financial income and expenses, the net nonoperating income was approximately NT$11.55 billion. For 2024, earnings per share (EPS) stood at NT$15.49 and the Board of Directors approved the earnings distribution plan, proposing a cash dividend of NT$13.00 per share, equating to a dividend payout ratio of approximately 83.9%.
| Unit: New Taiwan Dollar (NTD) 1,000 | Item | 2024 | 2023 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct economic value generated | Operating Revenue | 1,410,755,659 | 1,085,611,052 |
| Other Income | 18,872,492 | 17,141,526 | |
| Economic value distributed | Cost of Goods Sold | 1,299,995,651 | 1,000,728,093 |
| Operating Costs | 49,137,972 | 41,338,808 | |
| Other Costs | 7,327,879 | 8,959,651 | |
| Payments to government by country | 12,883,718 | 11,242,886 | |
| Economic value retained | 60,282,931 | 40,488,586 | |
2.3.2 Tax Policy
Quanta places great importance on tax governance and compliance, regarding the honest payment of taxes as one of the fundamental responsibilities that a corporation must fulfill. To enhance the quality of corporate governance, strengthen risk management, and respond to global trends in tax regulation, Quanta has clearly established a tax governance framework and principles, covering aspects such as regulatory compliance, risk control, and information transparency. The Board of Directors is the highest supervisory body for tax governance, and the head of the Financial Center is the chief executive responsible for coordinating the Group's tax management and information disclosure. The core principles of Quanta's tax management are as follows:
-
Regulatory Compliance and Integrity Filing
Comply with the tax regulations and legislative intent of the countries or regions where each operational site is located, accurately file tax returns within the statutory deadlines, and pay taxes on time to ensure lawful tax payment and the implementation of internal control mechanisms.
-
Principle of Substantive Taxation and Business Integrity
All commercial activities should have a reasonable operational substance and business purpose, avoiding the use of non-substantive tax structures for tax avoidance, thereby implementing the spirit of business integrity.
-
Management of Related Party Transactions and Transfer Pricing
Transactions between related enterprises should adhere to the arm's length principle and be documented in accordance with the Transfer Pricing Guidelines of the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) as well as the transfer pricing regulations of the tax jurisdictions where the related enterprises operate. Profit shifting for tax avoidance purposes is prohibited, and the use of tax havens for tax evasion is not permitted.
-
Transparency in Information Disclosure
Tax information and financial statements should be disclosed truthfully in accordance with accounting and tax-related laws and regulations, ensuring consistency, traceability, and transparency of the information to meet the expectations of stakeholders.
-
Professional Competency Development
Actively enhance the professional capabilities and compliance awareness of the tax team through regular training sessions, strengthen understanding of regulatory changes, and establish contingency mechanisms to promptly respond to potential impacts.
-
Regulatory Authority Relationship Management
Establish a communication mechanism with tax authorities based on mutual trust, respect, and integrity; proactively clarify uncertain tax issues; and maintain a positive and stable communication relationship.
-
Risk Identification and Management
Continuously monitor changes in international and local regulations as well as potential contentious issues, carefully assess the tax risks involved in operational activities, and implement corresponding control measures to reduce overall tax risk.
Quanta will continue to enhance the transparency of tax governance, optimize the identification and response capabilities for risks in multinational operations, ensure alignment between tax strategies and corporate business models, and support the Company's long-term stable development and the establishment of social trust.
2.3.3 Participation in External Public Associations
Quanta upholds the principle of political neutrality. In 2024, the Company made no political contributions and did not engage in any political lobbying activities. The Company actively participates in various industry associations and public organizations, establishing positive engagements through cross-sector platforms. These engagements promote industry exchange, technological innovation, and sustainable development. Focus areas include environmental sustainability, supply chain resilience, talent development, and digital transformation, with the aim of amplifying positive impact through collective action.
Regarding the public associations in which Quanta participates, the Company will conduct rolling reviews based on the level of substantive involvement and the relevance of the issues. It carefully evaluates whether their positions align with international carbon reduction initiatives and sustainability values, such as the Paris Agreement, to ensure that all engagements remain consistent with Quanta's commitments to climate change and corporate responsibility.
The main public associations currently joined by Quanta are as follows:
- Taipei Computer Association (Quanta Computer)
- Cloud Computing and IoT Association in Taiwan
- Taipei Computer Association (Quanta Cloud Technology Inc.)
- Dafeng (Shanghai) Computer Co., Ltd. Labor Union
- Songjiang Federation of Trade Unions of Economic and Technological Development Zone
- Women's Workers Committee of the General Labor Union of Songjiang District
- Songjiang District Intellectuals Association
- Shanghai Songjiang Safety Production Association
- Shanghai Fire Protection Association
- Shanghai Songjiang District Environmental Protection Technology Enterprises Association
- Responsible Business Alliance (RBA)
- Index Nuevo León, the Foreign Trade Manufacturing Association of Nuevo León, Mexico
- Environmental Quality Monitor Committee of Taiwan HwaYa Technology Park
Quanta will continue to actively participate in sustainability initiatives through industry alliances and local exchange platforms, promoting knowledge sharing and joint actions among enterprises, thereby expanding positive influence on issues related to climate change, sustainable governance, and social responsibility.
2.4 Supply Chain Management
Quanta places great importance on the critical role of the supply chain in corporate sustainable development, continuously enhancing its overall stability and resilience through institutionalized management and collaborative partnerships. Beyond fundamental quality and delivery management, Quanta progressively integrates Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) principles into supply chain operations, encouraging suppliers to improve responsible governance and sustainability awareness, thereby establishing long-term, trust-based, and mutually beneficial partnerships.
2.4.1 Quanta Value Chain
Quanta is a global leader in the development and manufacturing of electronic products, designing and assembling products based on customer requirements and delivering finished goods to designated locations for sale. The Company's value chain covers the complete process from product development, component procurement, and manufacturing to final delivery, with a commitment to providing competitive, highquality electronic solutions. Quanta's suppliers operate across multiple key technology fields and span both upstream and downstream manufacturing processes. These suppliers possess strong technical and manufacturing capabilities and are located in Taiwan, the United States, Japan, South Korea, China, Thailand, Mexico, and Europe. As of 2024, the total number of suppliers reached 2,029. Quanta's supply chain management strategy is driven by the overall competitiveness of suppliers, with evaluation criteria including price, research and development capabilities, manufacturing and quality performance, delivery reliability, and sustainability performance.
Localized Procurement
To reduce supply chain risks, lower carbon emissions, and enhance operational resilience, Quanta continues to advance its supply chain localization strategy by increasing the proportion of procurement from nearby regions at each manufacturing site. This approach also strengthens partnerships with suppliers.
In 2024, localization procurement rates (measured by procurement value) reached 34.22% for operations in Mainland China and 82.98% in the United States, with a global average of 37.3%. Moving forward, Quanta will further optimize supplier distribution and raise the share of local sourcing as a key driver for building a sustainable supply chain.
| Operational Site | Localization Procurement Ratio |
|---|---|
| Taiwan Site | 9.50% |
| China Site | 34.22% |
| Thailand Site | 2.61% |
| Vietnam Site | 9.44% |
| United States Site | 82.98% |
| Germany Site | 0.14% |
| Mexico Site | 2.14% |
Supply Chain Quality Management
Suppliers are key business partners and quality stakeholders for Quanta. Their performance in areas such as environmental protection, labor practices, human rights protection, social impact, and compliance with local regulations directly or indirectly impacts Quanta's operational stability, product quality and delivery timelines, and corporate reputation. To ensure that supply chain performance aligns with the Company's objectives, Quanta has established a rigorous supplier management framework covering new supplier assessments and annual audits, thereby strengthening risk control and fostering sustainable value creation among its partners. During the new supplier selection process, Quanta applies 13 comprehensive evaluation criteria, including quality systems, customer requirements, and design and development control. Sustainability topics such as "Environmental and Social Responsibility" and "Green Product Management" are incorporated as equally weighted assessment indicators alongside traditional manufacturing capabilities. Through a multi-dimensional review and guidance mechanism, Quanta ensures that its partners uphold quality, environmental stewardship, and social responsibility, equipping them with the comprehensive capabilities needed to support sustainable development.
Following evaluation, new suppliers are classified into three categories: Qualify, Conditional Qualify, and Unacceptable. Evaluation results are communicated through direct audits or bilateral engagement. Where deficiencies are identified, a Supplier Corrective Action Report (SCAR) is issued, and suppliers must submit an improvement plan or results report within the specified timeframe. If improvements require longterm measures-such as amendments to procedures or equipment upgrades-these are addressed through separate discussions and tracked under follow-up mechanisms. In addition, Quanta explicitly identifies and manages high-risk human rights issues during new supplier audits, including child labor, the employment of underage workers in hazardous operations, and forced or compulsory labor. If a supplier is found to violate labor and human rights standards and cannot resolve the issue within the specified timeframe, they will be disqualified from becoming an approved Quanta supplier.
In 2024, the audit completion rate for new suppliers at QCI, QSMC, and QCMC reached 100%. The number of required and completed audits for new suppliers at each site is shown in the table below.
| Operational Site | Number of Audits Required for New Suppliers | Number of Completed Audits | Completion Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| QCI | 353 | 353 | 100% |
| QSMC | 1621 | 1621 | 100% |
| QCMC | 114 | 114 | 100% |
| Indicators | |
|---|---|
| Quality System | Establish and maintain a comprehensive quality management system. |
| Customer Requirements | To thoroughly understand and meet the customer's demands and expectations regarding production scheduling. |
| Design and Development Control | Ensure that product quality and functionality meet standards throughout the design to mass production stages. |
| Document Control | Properly manage version control and records of quality documents to ensure information accuracy and traceability. |
| Supplier Management | Evaluate and monitor supplier quality performance to ensure the stability of raw materials and services. |
| Inspection and Testing | Perform inspections and testing on incoming materials, processes, and finished products to ensure compliance with quality standards. |
| Instrument Calibration | Conduct regular calibration of measurement instruments to ensure data accuracy and reliability. |
| Defective Product Control | Identify, isolate and properly dispose of defective products to prevent them from reaching customers and causing losses. |
| Quality Control | Comprehensive supervision of process quality to reduce defect rates and enhance product competitiveness. |
| Environmental and Social Responsibility | Comply with environmental protection and labor regulations, and actively fulfill corporate social responsibility. |
| Process Control | Monitor and optimize manufacturing processes to ensure stable production and consistent quality. |
| Green Product Management | Promote the use of non-hazardous substances in compliance with environmental regulations and green product standards. |
| Automotive Product Control | Conduct high-standard management in accordance with automotive industry regulations to ensure safety and durability. |
| Results | |
|---|---|
| Qualify | Fully meets the standards and is included in the list of qualified suppliers. |
| Conditional Qualify | Included in the list under specific conditions, such as being limited to supplying certain customers, part numbers, or products. |
| Unacceptable | Does not meet the standards and cannot be included in the list of qualified suppliers. |
In addition to onboarding new suppliers, Quanta also carries out annual audits for existing suppliers at its QCI, QSMC, and QCMC facilities. Through a structured audit process, the Company can promptly identify potential risks, drive continuous improvement, and foster responsible governance among suppliers-jointly establishing a stable and resilient supply chain system.
2.4.2 Sustainable Supply Chain Management
With growing global expectations for corporate sustainability, the management of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) risks within the supply chain has become a critical business priority. In recent years, market expectations for corporate supply chain responsibility have risen steadily, with increasing requirements for companies to implement Human Rights Due Diligence (HRDD). The European Union's Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CSDDD), which came into effect in 2024, further advances systematic governance based on the Human Rights and Environmental Due Diligence (HREDD) framework. Taiwan has also begun requiring companies to disclose greenhouse gas emissions data covering Scope 1 through Scope 3, strengthening the identification and management of supply chain carbon emissions. In addition, international clients now integrate supply chain sustainability performance into partnership evaluations and require suppliers to pass recognized audits such as those conducted by the Responsible Business Alliance (RBA). In response to growing stakeholder attention on sustainability, Quanta will continue to deepen sustainable supply chain management, enhance risk control and compliance capabilities, and strengthen the overall resilience and sustainable value of the supply chain.

Quanta has established a "Supplier Sustainability Code of Conduct," centered on business integrity and responsible commercial practices. Suppliers must comply with applicable laws and international standards such as the RBA Code of Conduct, covering topics including-but not limited to-fair trade, anti-corruption, personal data protection, intellectual property rights, and export controls. In 2024, Quanta conducted UFLPA (Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act) compliance investigations for targeted suppliers to ensure the supply chain is free from activities that could trigger legal risks. On the environmental side, Quanta requires suppliers to actively advance energy-saving and carbon reduction initiatives and disclose greenhouse gas emissions data. On the social side, suppliers must fulfill their human rights due diligence obligations toward the Company and, where necessary, provide supporting certifications and documentation to minimize and eliminate human rights risks across the supply chain. For critical raw materials, Quanta mandates sourcing from smelters or refiners certified by the Responsible Minerals Initiative (RMI) or the London Bullion Market Association (LBMA), thereby supporting responsible mining and avoiding conflict mineral concerns.
In supplier management, Quanta is building a supplier sustainability evaluation and carbon management platform, implementing it in phases. For potential suppliers, sustainability background checks will cover ISO certifications, sustainability management systems, carbon reduction initiatives, and human rights strategies. New suppliers must sign the Supplier Code of Conduct, complete a sustainability self-assessment, and undergo audit verification. Key existing suppliers are required to complete sustainability self-assessments and supply chain risk evaluations, with higher-risk suppliers subject to on-site or remote audits. A results management mechanism is used to track ongoing improvements. Minor deficiencies will be addressed through guidance and corrective measures, while major deficiencies may result in termination of cooperation.
By the end of 2024, a total of 1,038 suppliers had signed Quanta's RBA Compliance Declaration-994 before 2024 and 44 added during the year-achieving the annual target and demonstrating shared commitment to sustainability.
To further ensure CSR compliance, Quanta conducted CSR questionnaires and on-site or remote audits across all sites. In 2024, questionnaires were distributed to 80 Tier 1 material suppliers, 102 Tier 2 material suppliers, and 50 service suppliers, with CSR audits completed. Among them, 51 suppliers had already implemented RBA or SA8000 standards, confirming their practices and performance in labor rights, environmental protection, ethical business conduct, and management systems.
CSR Questionnaire Distribution Statistics
| Operational Site | Material Suppliers | Service Suppliers | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tier 1 supplier | Tier 2 supplier | |||
| QCI | 7 | 21 | 12 | 40 |
| QSMC | 25 | 0 | 16 | 41 |
| QCMC | 35 | 81 | 11 | 127 |
| Other Asia Sites | 3 | 0 | 6 | 9 |
| United States Site | 10 | 0 | 3 | 13 |
| Europe Sites | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| Total | 80 | 102 | 50 | 232 |
CSR Audit Deficiencies Statistical Report
| Operational Site | E Environmental Audit Deficiencies | S Social Audit Deficiencies | G Governance Audit Deficiencies | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| QCI | 6 | 18 | 1 | 25 |
| QSMC | 21 | 194 | 7 | 222 |
| QCMC | 17 | 269 | 14 | 300 |
| Other Asia Sites | 58 | 0 | 60 | 118 |
| United States Site | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Europe Sites | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 46 | 539 | 22 | 607 |
CSR Audit Statistical Report
| Operational Site | Material Suppliers | Service Suppliers | Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tier 1 supplier | Tier 2 supplier | ||||||
| RBA or Third- Party Audited | Quanta CSR Audited | RBA or Third- Party Audited | Quanta CSR Audited | RBA or Third- Party Audited | Quanta CSR Audited | ||
| QCI | 6 | 1 | 9 | 12 | 0 | 12 | 40 |
| QSMC | 13 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 16 | 41 |
| QCMC | 20 | 15 | 3 | 78 | 0 | 11 | 127 |
| Other Asia Sites | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 9 |
| United States Site | 0 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 13 |
| Europe Sites | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| Total | 39 | 41 | 12 | 90 | 0 | 50 | 232 |
Follow-up Actions for CSR Supplier Audits Statistical Table
| Operational Site | Total Number of Audited Suppliers | Suppliers Completed Rectification | Suppliers in Ongoing Rectification | Suppliers Terminated |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| QCI | 40 | 37 | 3 | 0 |
| QSMC | 41 | 38 | 3 | 0 |
| QCMC | 127 | 104 | 23 | 0 |
| Other Asia Sites | 9 | 8 | 1 | 0 |
| United States Site | 13 | 13 | 0 | 0 |
| Europe Sites | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Total | 232 | 202 | 30 | 0 |
Supply chain communication and transparency are also key priorities for the Company. To this end, Quanta has established a supplier grievance and whistleblowing mechanism and publicly discloses contact information for each manufacturing site on its official website. This mechanism enables stakeholders to report potential violations and risks. To ensure accountability extends throughout all levels of the supply chain, Quanta requires suppliers to proactively communicate whistleblowing mechanism details to their subsuppliers and subcontractors. Relevant responsibility clauses are also embedded in contracts with subcontractors to reinforce principles of integrity management and sustainable governance.
Human Rights Risks and Management of Suppliers
Forced Labor
During audits and inspections of suppliers, working hours and the absence of forced labor remain key focus areas. Quanta addresses these issues through daily communication and oversight to strengthen suppliers' awareness and enforcement of the Code of Conduct. Suppliers are strictly prohibited from engaging in any human rights violations; in the event of a serious violation that cannot be rectified, the business relationship will be terminated.
Forced labor risks are often found within labor dispatch arrangements and foreign migrant worker agencies. To ensure dispatched workers receive equal protections as regular employees, Quanta sites sign a "Labor Dispatch Agreement" with labor dispatch agencies that outlines mutual responsibilities, including equal pay, equal social benefit contributions, and workplace safety. Quanta also reduces human rights risks by directly paying wages and benefits to workers.
At QCI, which employs foreign migrant workers, a "zero-fee policy" and robust due diligence process ensure that no recruitment fees are charged to workers, safeguarding their basic rights.
In terms of management execution, the Company conducts diverse methods, including on-site audits at supplier factories, employee interviews, and written surveys, to verify whether the policies of non-discrimination and non-forced labor are implemented. In particular, the factories in mainland China require labor dispatch companies to display anti-discrimination posters. The CSR department, in a joint task force, conducts antidiscrimination surveys for new employees. This is complemented by employee training and interviews to ensure that all employees―whether directly hired by the company or from a labor dispatch firm―are not subject to differential treatment based on non-jobrelated factors, and that they are not required to pay any recruitment fees.
Supplier Human Rights Due Diligence
In response to the EU's Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive and growing international emphasis on human rights in supply chains, Quanta has reinforced its due diligence practices. Guided by the principles of the Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act, the Company has developed a more comprehensive mechanism to assess suppliers' labor treatment, child labor prevention, freedom of employment and association, and recruitment practices. This initiative not only fulfills corporate social responsibility but also helps prevent and mitigate human rights risks across the supply chain.
Responsible Mineral Management
In conflict-affected and high-risk areas such as the Democratic Republic of the Congo, non-state armed groups control the mining and trade of minerals including Au, Ta, W, Sn, Co, and mica, causing severe social, environmental, and human rights impacts. Quanta's Conflict Minerals Management Policy commits to avoiding any support for such activities. Following the OECD Due Diligence Guidance and RMI standards, Quanta requires suppliers to submit the Conflict Minerals Reporting Template (CMRT) and Extended Mineral Reporting Template (EMRT), and demands that upstream smelters/refiners be certified by third-party organizations such as RMI or LBMA.
From the perspective of international industry trends, the Responsible Minerals Initiative (RMI) and customers have clear requirements for due diligence and risk management for two minerals in the supply chain: cobalt and mica. In response, Quanta has established a conflict minerals management policy, committing not to support any activities that would lead to the deterioration of social conditions, the environment, or human rights. At the same time, the Company follows the OECD Due Diligence Guidance for Responsible Supply Chains of Minerals and the RMI standards, requiring suppliers to submit the Conflict Minerals Reporting Template (CMRT) and the Extended Mineral Reporting Template (EMRT). The Company also requires upstream smelters/refiners in the supply chain to actively participate in certification by independent third-party organizations such as the RMI or the London Bullion Market Association (LBMA).
Overview of Quanta's 2024 Due Diligence Investigation
1. Preparatory Stage
- Clearly identify the investigation targets, verify the contact windows for the investigation targets, determine the internal procurement personnel responsible for the investigated suppliers, and take charge of upgrading and optimizing the responsible mineral procurement management system.
- The Company identified and investigated material suppliers that may use cobalt and mica in 2024.
2. Investigation Stage
- Send the due diligence system link to the suppliers and notify the corresponding internal procurement responsible personnel to more efficiently follow up on the investigation status. When risks are identified, continue to communicate with the suppliers to control and eliminate the related risks.
- In addition to CMRT, the Company also sends the due diligence system link to suppliers for EMRT investigation and requires suppliers to use the latest version of EMRT disclosed on the RMI official website to report information on the two minerals, cobalt (Co) and mica.
- The CSR department conducts regular checks on the RMI and LBMA official websites to confirm compliant smelters and updates the latest results to the responsible mineral procurement management system for effective management of compliant smelters. Furthermore, on a quarterly basis, the Company issues investigation notices to suppliers who either submit non-compliant CMRTs or fail to respond.
3. Supplier Report Summary Tracking Stage
- This year, Quanta not only completed the due diligence tasks but also utilized the Responsible Minerals Procurement Management System's CMRT and EMRT quarterly update notification functions, CMRT and EMRT annual update notification functions, CMRT non-compliance/compliance notification functions, and the CMRT vendor code lock reminder function for overdue effective date updates, in order to better and continuously provide suppliers with effective information.
4. Supplier Report Analysis and Risk Mitigation Measures
- The Responsible Mineral Procurement Management System can analyze due diligence reports submitted by suppliers and generate summary reports, including the overall response status of suppliers and the due diligence information disclosed by them. The company's responsible unit then analyzes potential issues based on this data. For critical materials that could pose a significant risk to our operations (such as high-carbon raw materials and specific imported components), the Company implements strategies like diversifying suppliers, introducing alternative materials, and strengthening supplier due diligence. This helps us reduce the risks of supply chain disruption, price volatility, and compliance issues. Subsequently, the Company can combine summary reports to provide customers with CMRT and EMRT due diligence reports upon request.
- For the risks identified during the investigation, the Company refer to the "OECD Due Diligence Guidance for Responsible Supply Chains of Minerals" and combined with actual circumstances. Suppliers will be required to procure alternative materials or obtain certification, and if necessary, terminate relationships with the suppliers.
Quanta's 2024 Responsible Mineral Procurement Annual Results
- In 2024, 99.36% of suppliers have signed the Quanta Supplier Responsible Mineral Sourcing Compliance Statement as required.
- For the CMRT part, 99.36% of suppliers submitted/updated CMRT as required by our company.
- For the EMRT part, 98.66% of suppliers submitted or updated EMRT as required by our company.
- Based on the responsible mineral procurement supplier online training launched in 2023, the Company conducted one annual update online training in 2024, and the attendance rate of suppliers reached 60.17% (counted by the registered online training username).
| 2024 | Number of Suppliers Targeted for Engagement | Number of Suppliers Engaged in 2024 | Engagement Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Signing Rate of "Supplier Responsible Mineral Procurement Compliance Declaration" | 1,402 | 1,393 | 99.35% |
| CMRT Submission/ Update Rate | 1,402 | 1,393 | 99.36% |
| EMRT Submission/ Update Rate | 749 | 739 | 98.66% |
| 2024 | Number of registrations | Number of Attendees | Attendance Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplier Training | 1,436 | 864 | 60.17% |
2.5 Products and Clients
Quanta places clients at the center of its operations, committed to providing high-quality, innovative, and sustainable products and services, while continuously strengthening cooperative relationships with global clients. Through quality management, green design, client satisfaction surveys, and real-time communication mechanisms, Quanta continuously optimizes user experience and product reliability, collaborating with clients to jointly advance industry innovation and sustainable transformation.
2.5.1 Green Product Design
Quanta is deeply aware of its environmental responsibilities and influence within the supply chain. Therefore, it actively leads transformative efforts centered on green design principles, comprehensively considering the environmental impacts at every stage of the product life cycle-from design and production to use and recycling. The Company systematically evaluates and optimizes product design to reduce carbon emissions and resource consumption. By selecting low-impact materials, strengthening supply chain transparency, and incorporating reduction-oriented and modular design strategies, Quanta effectively reduces environmental impact and carbon footprint. Furthermore, products are designed to meet energy efficiency standards such as ENERGY STAR, equipped with low-power consumption modes, and engineered for enhanced durability and extended service life-making sustainable practices more accessible in daily use. At the same time, Quanta strictly complies with regulatory requirements related to product health and safety, information labeling, and customer privacy. As of the reporting period, there were no incidents of non-compliance with regulations concerning product and service health and safety, no violations related to product information and labeling requirements, and no confirmed complaints regarding customer privacy breaches or data loss-demonstrating the Company's strong commitment to product compliance and information management.
On this basis, Quanta continues to strengthen every aspect of product design to ensure that the green concept is deeply embedded in all stages of the product life cycle. The Company is committed to achieving sustainable goals that combine high performance and environmental friendliness across the entire product line. This is actively implemented through the introduction of designs that are easy to disassemble and the promotion of recycling and reuse programs, thereby effectively realizing the concept of a circular economy. By addressing each phase of the product life cycle-from material selection and design processes to end-of-life recycling management-Quanta ensures that every stage contributes to greater resource efficiency and environmental sustainability. Through these efforts, the Company creates long-term value on the path toward sustainable development, achieving both enhanced corporate responsibility and strengthened competitiveness.
Green Product Design Strategy
Quanta has long been committed to the research and development of green products, striving to integrate environmentally friendly concepts into the design of the entire product life cycle. To enhance the effectiveness of green design, the Company adopts a systematic approach across six core dimensions, optimizing material selection, structural design, and recycling applications. The following will explain how Quanta implements a product strategy that simultaneously achieves high performance and low environmental impact through these six major aspects.
1. Product Material and Chemical Composition Control
Quanta's "Full Materials Declaration (FMD) System" supports a wide range of data exchange formats and can generate outputs that comply with various international standards, such as IPC-1752A and IEC 62474, based on individual client requirements. This ensures seamless integration with client systems. The system can quickly consolidate relevant data to provide compliance reports that meet various customer requirements and regulatory standards, effectively enhancing supply chain compliance management efficiency and reducing overall operation time. Through the FMD system, Quanta also works closely with supply chain partners to collect detailed information on chemical substances, including their usage and quantities. This not only helps mitigate risks related to hazardous substances and strengthens chemical management capabilities across the supply chain but also enables in-depth material composition analysis. As a result, the Company can proactively identify optimization opportunities and support suppliers in sourcing safer alternative materials.
As the management mechanism has matured, FMD has been fully implemented since June 2024 across all parts and materials, further enhancing Quanta's material management capabilities in collaboration with its suppliers and improving supply chain transparency and compliance. Currently, numerous suppliers are actively participating in the FMD system, providing chemical substance lists for materials. To date, more than 120,000 approved component records have passed the review process. Quanta will continue to expand the application of the FMD system and strengthen green material management across the supply chain to ensure full compliance with international environmental regulations.
2. Quanta Green Design Standards and Supply Chain Compliance Management
Quanta continuously monitors and analyzes the latest developments in international regulations, actively respond to various countries' restrictions on PFAS, and pays close attention to updates and implementation schedules of the EU Battery Directive, the EU REACH Substances of Very High Concern (SVHCs), and packaging material regulations. These regulatory requirements are incorporated in advance into the standard specifications for product development. All parts and materials must comply with the Quanta General Material Specification - Substances Restricted for Use before entering the product design and manufacturing processes.
Simultaneously, to enhance the supply chain's awareness and responsiveness to green regulations, Quanta regularly holds supplier conferences to promote green supply chain management, carbon reduction strategies, and regulatory trend awareness. Through surveys and interactive meetings, Quanta accurately assesses suppliers' current status, effectively communicates key information, and provides necessary support. These efforts help reduce the environmental impact of products and safeguard consumer health and safety.
2024 Focus Areas and Management Measures
A. Prohibited Substances List
- According to Annex 17 of REACH, international environmental protection conventions, and client requirements, mandatory restrictions and prohibitions are imposed on the addition of certain proportions of banned substances.
B. Halogen-free Requirements
- Strict controls are implemented over the use of brominated and chlorinated flame retardants and halogen-containing materials for certain clients and product components to prevent unnecessary environmental pollution.
C. Restricted Substances for ME/EE Components
- In compliance with the EU RoHS Directive, restricted substances in mechanical and electronic components are controlled to ensure that products meet international environmental standards.
D. Restricted Substances for Batteries and Battery Packs
- In compliance with international battery directives and related regulations, comprehensive control is implemented over the content of chemical substances, labeling, and management requirements.
E. Restricted Substances for Packaging Materials
- According to major international packaging material regulations, restrictions are established on regulated substances in packaging materials to reduce the use of non-recyclable and harmful substances.
F. Future Reduction Substances
- Continuously monitor regulatory trends in various countries, environmental conventions, and client requirements. Proactively manage and respond to chemical substances that are soon to be regulated by implementing early control measures. Actively require the supply chain to disclose relevant components and conduct advance evaluations of alternative materials and technologies to gradually reduce the use of such substances.
G. REACH SVHCs Requirements
- In response to the biannual updates of the EU REACH SVHCs list, the supply chain is promptly notified to ensure the legal compliance of product components.
H. PFAS Management
- Tracking global regulatory developments on PFAS control, including TSCA reporting requirements for PFAS and the latest provisions of EPEAT 3.0.
- Conduct a comprehensive investigation of the usage status of PFAS in products, promote manufacturers to select PFAS-free materials, and evaluate alternative materials.
3. Use of Sustainable Materials
Quanta incorporates sustainable materials into the core of product design, prioritizing the use of materials that are sourced from recycled content, have low environmental impact, and possess reusable characteristics. Particularly in plastic and metal components, continuously increase the proportion of recycled materials used to promote resource circularity and material efficiency. The primary sources of recycled materials include:
- PCR (Post-Consumer Recycled): Plastics discarded by consumers after use, collected, cleaned, and reprocessed into new materials.
- PIR (Post-Industrial Recycled): Waste generated during manufacturing, recovered and reused before consumer use.
- OBP (Ocean-Bound Plastic): Plastic waste at risk of entering oceans, collected to reduce marine pollution.
A. Plastic Materials
Depending on functional requirements, the proportion of recycled plastic ranges from 30% to 85%. The types of recycled plastics used include PC, PC/ABS, and ABS, mainly applied in critical components such as product casings, speakers, and fans.
B. Metal Materials
Incorporate recycled metals into the product's metal casing and mechanical components to reduce the environmental impact of mining and smelting processes. Currently, the applications of metal materials are as follows:
- Enclosure Materials: Recycled aluminum (50%-100%), recycled steel (10%)
- Internal Supports and Mechanical Components: Continuously increase the application ratio of recycled aluminum and recycled steel and actively evaluate the introduction of other recycled metals. Furthermore, regarding the management of the use of rare earth elements (such as Neodymium, Nd) and other critical metals, Quanta discloses material components through FMD to ensure supply chain transparency. The Company continuously explores ways to increase the application of recycled rare earth materials in components to reduce reliance on newly mined resources.

C. Modular Design and Recyclability
Through modular design, enhance the upgradability of products, enabling easy replacement and maintenance of components, thereby extending product lifespan and reducing resource consumption. Furthermore, recyclability is considered from the design phase. Optimized product design ensures easy disassembly to facilitate effective end-oflife recycling.
4. Packaging Material Reduction and Green Design
Quanta is committed to promoting innovation and reduction in packaging materials, actively eliminating unnecessary packaging and single-use plastics. Packaging design prioritizes recyclability, reusability, and material reduction principles, and gradually incorporates recycled materials. Through sustainable design orientation, reduce the overall environmental impact of packaging, and implement resource efficiency and product life cycle management.
A. Utilize Recycled Materials to Reduce Plastic Usage
Adopt recycled pulp and fiber-based materials as substitutes for conventional plastic and foam. These alternatives provide effective cushioning to ensure product safety during transportation while enhancing overall resource utilization efficiency. In order to further reduce the use of plastic, paper tape and pull-tab designs have been adopted to replace traditional packing tape, ensuring secure sealing while delivering improved environmental performance.
B. Reducing Packaging Volume, Enhancing Efficiency
By optimizing packaging design to minimize total volume and integrating multiple products into a single, efficient bulk package, Quanta reduces transportation volume and enhances logistics efficiency.
- Streamlined Lightweight Design: Optimized packaging dimensions and reduced packaging weight through structural engineering techniques, while ensuring product safety.
- Transition from single-item packaging to multi-item packaging: Consolidate multiple units into a single package to enhance storage and distribution efficiency.
- Reusable Packaging Model: An internal circular packaging reuse strategy has been implemented to minimize packaging waste across the supply chain.

5. Improving Energy Efficiency
Actively implement low power consumption strategies to effectively reduce energy consumption. This includes the adoption of low-power electronic components; the implementation of efficient power management technologies to dynamically adjust the device's power consumption during operation, thereby reducing energy use during standby and idle periods; the optimization of heat dissipation module design to enhance system efficiency and stability during operation while minimizing the additional energy required for cooling equipment; and the application of energy efficiency testing and monitoring to ensure that the product meets or exceeds international energy efficiency standards throughout both production and usage.
The products manufactured comply with multiple international energy efficiency standards for recognition and certification, including the European Union's ErP Lot 3, Lot 6/26, and Lot 9 directives, ENERGY STAR(r), the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Battery Charger System (BCS) specifications, and the requirements of Natural Resources Canada (NRCan).
6. Participation in Sustainable Labeling for Electronic Products and Sustainable Product Design
Quanta actively engages in internationally recognized sustainability certifications for electronic products, including EPEAT and TCO Certified. The Company not only incorporates existing standards into its green design blueprint but also monitors the development trends of new standards. Furthermore, Quanta collaborates closely with clients during the product design process, focusing on the following areas to enhance the sustainability value of its products:
A. Supply Chain Responsibility
Through supply chain investigations, ensure that partners comply with social responsibility and environmental responsibility standards, including the implementation of the RBA Code of Conduct, and actively promote energy management and environmental management, in order to reduce the environmental impact of the supply chain.
B. Sustainable Product Design
Quanta enhances the environmental performance of its products from the design stage by carefully selecting materials, improving maintainability and upgradability, and integrating rigorous reliability testing. It continuously optimizes the quality of materials, components and assembly to extend product life, maximizes the value of the circular economy and achieves sustainable use of resources.
C. Reduction of Hazardous Chemicals and Material Transparency
Enhance material transparency through FMD to ensure compliance with the latest global environmental regulations and standards and actively reduce the use of brominated and chlorinated flame retardants. Simultaneously, Quanta continues to monitor issues related to PFAS, identify its applications in products, and assess and mitigate potential impacts on the environment and health.
Product Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Certification
In response to market expectations for green products, Quanta continuously monitors and implements various labeling and certification mechanisms related to the sustainable performance of its products. These certifications not only signify recognition of the product's environmental performance but also help enhance consumer awareness and trust in sustainable products, thereby further strengthening the Company's responsible brand image and competitive advantage in the global market.
Product Sustainability Certification:
Quanta actively responds to the international mainstream standards for sustainable product certification, focusing on increasing the use of renewable energy in factories, enhancing the proportion of recycled materials, reducing the use of hazardous chemicals, and seeking safe alternatives to ensure that products achieve excellence in environmental friendliness and competitiveness. Through continuous innovation and optimization, Quanta's products have successfully obtained certifications including EPEAT, TCO, and TGM, significantly improving both environmental performance and market competitiveness. In 2024, Quanta further targeted the latest sustainability standards, including TCO Certified 10.0 and EPEAT 3.0. The Company actively worked with customers and suppliers to meet evolving requirements in social responsibility, sustainable materials, and hazardous substance management, ensuring strong environmental competitiveness across its product portfolio.
Number of products that obtained sustainable certification in 2024:
| Certification Type | Quantity |
|---|---|
| US Electronic Product Environmental Assessment Tool (US EPEAT) | 80 |
| TCO Sustainable Certification (TCO Certified) | 50 |
| Taiwan Green Mark (TGM) | 18 |
Energy Efficiency Certification:
Quanta is dedicated to improving energy efficiency during the product usage phase by adhering to relevant energy standards such as Energy Star. This is achieved through the integration of high-efficiency components, the implementation of low-power consumption modes tailored to various operating states, and the establishment of power consumption limits for standby, startup, and sleep modes-ensuring energy-efficient product design.
Number of energy efficiency certifications obtained in 2024:
| Certification Type | Quantity |
|---|---|
| Energy star | 74 |
| California Energy Commission (CEC) | 65 |
| New Zealand/Australia Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS) | 55 |
| Department of Energy - BCS Energy Efficiency (DOE BCS) | 25 |
| Korea E-Standby | 23 |
| China Energy Label (CEL) | 24 |
| Nature Resource Canada (NRCan) | 27 |
Expanding the Use of Sustainable Materials
Quanta continues to dedicate efforts to the integration of recycled materials, responding to clients' dual demands for product performance and sustainability. Taking plastic materials as an example, Quanta prioritizes the use of recycled content in products applying for EPEAT certification to meet client expectations for both performance and sustainability. Recycled plastics-ranging from 30% to 85% content-are widely incorporated into key components such as casings, speakers, and fans. The specific proportion of recycled plastic used varies by product category, as outlined below:
| Product Category | Proportion of Recycled Plastic Integration |
|---|---|
| NB (Notebook) | 2%~79% |
| DT (Desktop Computer) | 28% |
| AIO PC (All-in-One Computer) | 35%~69% |
Simultaneously, in the area of metal materials, the primary focus is on the application of recycled aluminum and recycled steel, utilizing 50% to 100% recycled aluminum and 5% recycled steel in metal casings and internal brackets. The primary recycled metal materials used include:
- ADC12: High-pressure die-cast aluminum alloy, 100% PIR
- AL6063: Aluminum-magnesium-silicon alloy, 75% PIR
- AL5052: Aluminum-magnesium alloy, 50% PIR
- BTRC5: Steel material incorporating recycled content, 5% PIR
In addition, Quanta serves as an Original Design Manufacturer (ODM), and the ownership of the final products belongs to the clients. Therefore, product recycling cannot be carried out by Quanta.
2.5.2 Customer Relationship Management
To strengthen long-term cooperative relationships with customers and accurately gauge service satisfaction, Quanta conducts a customer satisfaction survey each year in the fourth quarter through its business units using the "Customer Satisfaction Survey System". The survey collects feedback on key topics such as quality management and green products. This mechanism serves not only as a reference for the annual operational review but also as a key tool for continuous improvement in quality and environmental management, strategic planning, and stakeholder communication. The 2024 survey covered multiple dimensions related to product responsibility. By leveraging quantitative feedback and a structured anomaly tracking process, Quanta effectively enhances customer trust and value recognition.
Quality Management Satisfaction
According to the customer satisfaction survey results, Quanta's quality management encompasses six core aspects: product quality management effectiveness, service quality and attitude, speed and effectiveness of problem resolution, product development capability, product protection during transportation, and on-time delivery performance. These aspects comprehensively reflect the quality management performance of products and services from development and manufacturing to delivery. The overall satisfaction rate for quality management in 2024 reached 96%, indicating that Quanta has received high recognition from customers across all dimensions of quality management
Satisfaction Rate for Green Products
According to the 2024 Customer Satisfaction Survey, Quanta's Green Product Management was evaluated across six key dimensions: clarity and accessibility of communication channels, responsiveness to green product requirements, capability for hazardous substance detection, product compliance with customer specifications, effectiveness of control measures, and speed of abnormal event resolution. These criteria provide a comprehensive assessment of Quanta's performance in eco-friendly product design, regulatory compliance, and operational responsiveness. The overall satisfaction rate for 2024 reached 91%. Survey results show that customers highly appreciated Quanta's communication and control processes related to green products. However, some customers did not respond to the item on "abnormal incident handling speed," primarily because no such incidents occurred during the year, leaving them unable to provide relevant feedback. To improve the completeness of future surveys and the quality of customer participation, Quanta will provide clear, item-specific guidance during the questionnaire distribution phase. Assigned account managers will also proactively engage with customers to support the response process, ensuring that all evaluation dimensions accurately reflect management performance and customer expectations.
In response to feedback and suggestions collected through customer surveys, Quanta has implemented a mechanism for immediate response and improvement. The results are regularly consolidated and analyzed during management reviews to inform adjustments to the focus areas of quality and green product management for the following year, thereby continuously enhancing overall service quality and product delivery performance. Through this continuous improvement cycle, Quanta strengthens trust-based relationships with customers and deepens long-term partnerships grounded in sustainable values, establishing a key foundation for the Company's sustainable business operations.